Financial risk management is an essential discipline that helps organizations navigate the complex landscape of financial uncertainties. It involves identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks that can adversely affect a company’s financial performance. With various types of financial risks, including market risk, credit risk, operational risk, and liquidity risk, understanding their implications can significantly enhance decision-making processes.
This field not only emphasizes the importance of quantitative techniques and regulatory frameworks but also highlights the role of technology in transforming risk management practices. By leveraging advanced tools and methods, organizations can better prepare themselves for potential financial pitfalls and adopt effective strategies for long-term stability.
Understanding the Core Concepts of Financial Risk Management
Financial risk management is a vital aspect of finance that focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that can negatively impact the financial performance of an organization. The primary objective is to minimize potential losses while maximizing opportunities for profit. This involves both qualitative and quantitative analysis to ensure that financial decisions are made with an understanding of the associated risks.
By implementing effective risk management strategies, firms can maintain stability, protect assets, and enhance shareholder value.
Types of Financial Risks
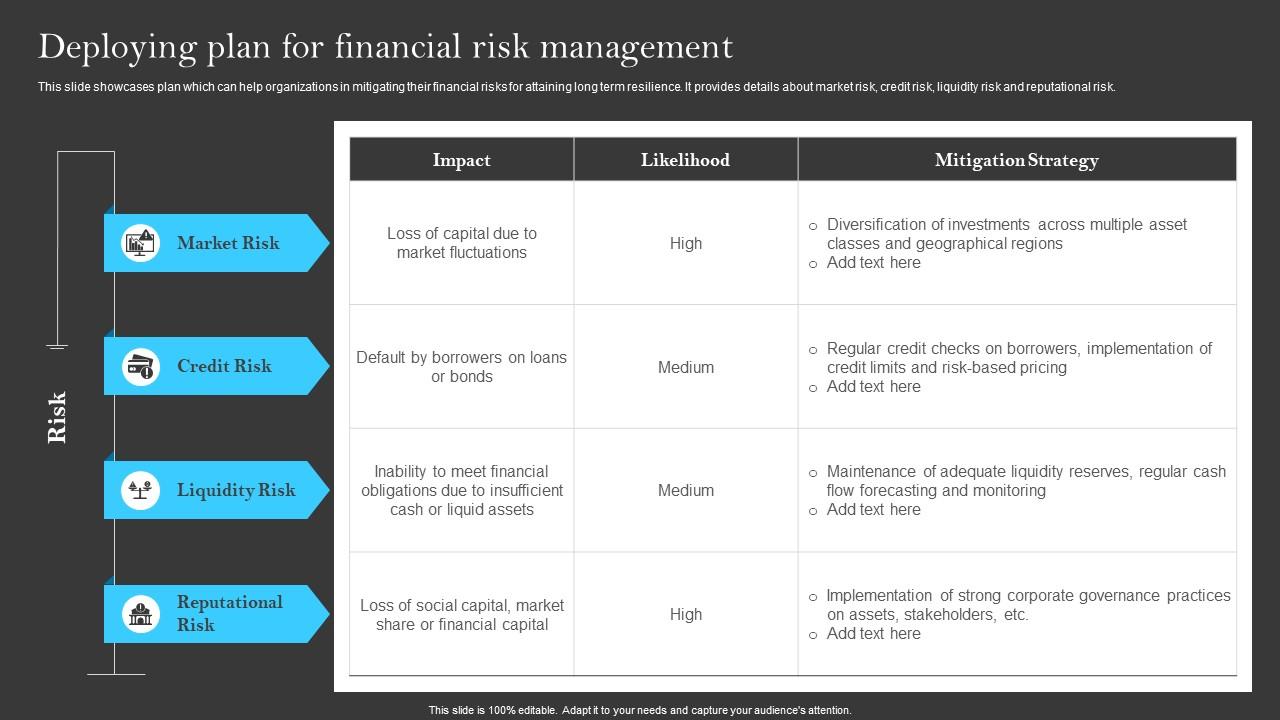
Different types of financial risks can affect organizations in various ways. Understanding these risks is crucial for developing robust risk management strategies. Below are the key categories of financial risks, along with notable examples for clarity:
- Market Risk: This risk arises from fluctuations in the market prices of assets. For instance, a sudden drop in stock prices can lead to significant losses for investors. An example is the 2008 financial crisis, where the collapse of housing prices triggered widespread losses in mortgage-backed securities.
- Credit Risk: This relates to the possibility that a counterparty will default on a financial obligation. For example, if a corporation fails to repay its bonds, the investors incur a loss. The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers in 2008 is a stark illustration of credit risk materializing.
- Operational Risk: This encompasses risks arising from failed internal processes, systems, or external events. A typical example includes a data breach that compromises sensitive customer information, leading to financial losses and reputational damage.
- Liquidity Risk: This is the risk that an entity will not be able to meet its short-term financial obligations due to an inability to convert assets into cash quickly. For instance, during a market downturn, a company may struggle to sell its inventory without incurring substantial losses.
Regulatory Frameworks in Financial Risk Management
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in shaping financial risk management practices across the globe. These regulations ensure that financial institutions operate within a structured environment designed to promote transparency, stability, and accountability. Key regulations include the Basel Accords, which set international standards for bank capital adequacy, stress testing, and market liquidity risk. Compliance with these frameworks helps organizations mitigate risks by implementing appropriate risk management processes and reporting standards.
Regulatory oversight ensures that firms are prepared for economic downturns and can protect the interests of stakeholders, including investors and customers.
“A prudent financial risk management strategy not only safeguards assets but also enhances competitiveness in the market.”
The Importance of Quantitative Techniques in Financial Risk Management

In today’s complex financial landscape, quantitative techniques play a crucial role in managing and assessing risk. These methods leverage mathematical models and statistical analysis to quantify potential losses, allowing institutions to make informed decisions. By applying quantitative techniques, financial managers can not only identify risks but also develop strategies to mitigate them effectively.
Quantitative Methods for Assessing Financial Risks
Among the various quantitative methods utilized in financial risk management, Value at Risk (VaR) and stress testing stand out as fundamental tools. VaR measures the potential loss in value of a portfolio under normal market conditions over a set time period, giving a snapshot of risk exposure. For instance, if a bank calculates a VaR of $1 million at a 95% confidence level over one day, it implies that there is a 5% chance the portfolio could lose more than $1 million on that day.Stress testing, on the other hand, involves simulating extreme market scenarios to evaluate how a portfolio would fare under adverse conditions.
This approach not only helps in understanding potential vulnerabilities but also assists in preparing robust response strategies. Both tools are critical in ensuring financial institutions remain resilient in the face of market fluctuations.
Statistical Tools and Models for Risk Measurement
A range of statistical tools and models supports risk measurement and management in the financial sector. Commonly used models include:
- Monte Carlo Simulation: This technique generates a large number of random scenarios to model uncertainties in asset prices, interest rates, and other financial variables. It provides a comprehensive view of potential outcomes, enhancing decision-making.
- GARCH Models: Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity (GARCH) models are utilized to forecast volatility in financial markets. They account for changing volatility over time, which is crucial for accurate risk assessment.
- Copulas: Copula functions allow for the modeling of dependencies between different financial instruments. This helps in understanding how correlated risks can impact overall portfolio risk.
These methods facilitate a deeper understanding of risk dynamics, ensuring that financial managers can implement effective strategies based on quantitative data.
Comparative Analysis of Traditional vs. Modern Quantitative Techniques
The evolution of quantitative techniques in financial risk management reveals significant differences between traditional and modern approaches. Traditional techniques often rely on historical data and simpler models that may not adequately capture complex market behaviors.In contrast, modern techniques incorporate advanced statistical analyses, computational power, and machine learning algorithms. These advancements allow for more accurate modeling of risks, particularly in volatile markets.
For instance, while traditional methods may employ a simple standard deviation to assess risk, modern approaches might integrate a combination of GARCH models and stress testing scenarios to predict future volatility more effectively.The table below summarizes key differences between traditional and modern quantitative techniques:
| Aspect | Traditional Techniques | Modern Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Data Utilization | Primarily historical data | Real-time and historical data combined |
| Complexity | Simpler models | Advanced statistical and machine learning models |
| Risk Assessment | Static measures (e.g., standard deviation) | Dynamically updated measures (e.g., VaR, stress tests) |
| Market Changes | Less responsive to rapid changes | Quick adaptation to new market conditions |
The shift from traditional to modern quantitative techniques marks a significant advancement in financial risk management, ultimately enhancing the ability to navigate uncertainties and protect financial assets.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Financial Risk Management
The integration of technology into financial risk management has become a game changer for businesses and financial institutions. With the rapid evolution of digital tools, organizations are not only enhancing their risk assessment processes but also improving their overall decision-making capabilities. The advent of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) has brought forth sophisticated methodologies that allow for better prediction, analysis, and management of financial risks.Technological advancements have significantly streamlined risk management processes, fostering efficiency and accuracy.
AI and ML algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns that may indicate potential risks. They facilitate real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, which empower organizations to make informed decisions swiftly. Such capabilities have reshaped traditional risk management practices, moving them from reactive to proactive strategies.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Risk Assessment
The impact of AI and ML on risk assessment is profound, providing tools that enhance accuracy and efficiency. These technologies process large volumes of data far beyond human capability, offering insights that are critical for effective risk management. Below are some key areas where AI and ML have made substantial contributions:
- Predictive Analytics: AI models can predict potential financial downturns by analyzing historical data patterns, enabling organizations to take preventive measures.
- Fraud Detection: Machine learning algorithms continuously learn from transaction data, helping to identify fraudulent activities in real-time and mitigate risks.
- Market Analysis: AI tools assess market trends and volatility, providing valuable data that aid in risk mitigation strategies.
- Credit Scoring: Advanced algorithms evaluate borrower risk more accurately than traditional methods, improving lending decisions and reducing default rates.
The adoption of software tools in the financial sector has further streamlined risk management. Some widely utilized tools include:
- RiskMetrics: This tool offers sophisticated risk modeling and quantitative analysis capabilities, enabling firms to manage market risks effectively.
- Moody’s Analytics: Known for its comprehensive risk assessment solutions, it provides credit risk management services and economic forecasting.
- Palantir: Utilized for its powerful data integration and analysis capabilities, it helps organizations manage complex risk scenarios.
- Tableau: While not exclusively for risk management, this data visualization tool assists in identifying trends and anomalies in financial data, facilitating better risk assessment.
Integrating technology within risk management practices comes with several benefits and challenges. The benefits include:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Automation reduces human error, leading to more precise risk assessments.
- Speed of Analysis: Real-time data processing allows for quicker response times to emerging risks.
- Cost Efficiency: Over time, advanced technologies can lower operational costs through improved efficiency.
However, challenges also exist, such as:
- Implementation Costs: Initial investments for advanced technology systems can be significant, potentially straining budgets.
- Data Security Concerns: With increased reliance on digital tools, safeguarding sensitive financial data against cyber threats is paramount.
- Talent Gap: There is often a shortage of skilled professionals who can effectively manage and interpret complex AI and ML systems.
The role of technology in enhancing financial risk management cannot be overstated, as it continues to revolutionize the way risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated. The ongoing evolution of these technologies promises even greater improvements and efficiencies in the future.
Developing an Effective Risk Management Strategy for Organizations
Creating a robust financial risk management strategy is crucial for organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of today’s financial landscape. A well-structured approach not only helps in identifying potential risks but also equips organizations with the tools to mitigate them effectively. This process ensures that financial uncertainties are managed proactively, safeguarding the organization’s assets and ensuring long-term sustainability.The framework for developing an effective financial risk management strategy involves several key steps that organizations can follow systematically.
By adhering to this framework, organizations can establish a solid foundation for identifying, assessing, and managing financial risks.
Step-by-Step Framework for Financial Risk Management
The following steps serve as a valuable guideline for organizations to craft their financial risk management strategies:
- Identify Risks: Begin with a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential financial risks affecting the organization. This includes market risks, credit risks, operational risks, and liquidity risks.
- Assess Risks: Evaluate the identified risks in terms of their likelihood and potential impact on the organization. Performing quantitative and qualitative analyses can help prioritize the risks effectively.
- Develop Strategies: Formulate strategies to mitigate the assessed risks. This may involve diversifying investments, implementing hedging strategies, or adjusting operational practices.
- Implement Controls: Establish policies and procedures to enforce the risk management strategies. This includes setting limits on exposure and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the risk management strategies and revise them as necessary. Continuous assessment is vital to adapting to evolving financial conditions.
Key Stakeholders in the Risk Management Process
Identifying and engaging key stakeholders is essential for effective risk management. Each stakeholder plays a specific role in ensuring that the risk management framework is executed successfully.
“Collaboration among stakeholders enhances the organization’s resilience to financial risks.”
The following stakeholders are typically involved in the risk management process:
- Board of Directors: Provides oversight and ensures that risk management practices align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Executive Management: Responsible for implementing the risk management strategy and integrating it into the organization’s operations.
- Risk Management Team: Focuses on identifying, assessing, and monitoring risks, and ensures compliance with risk policies.
- Finance Department: Plays a crucial role in analyzing financial risks, including credit and liquidity risks, and ensuring financial reporting accuracy.
- Internal Audit: Evaluates the effectiveness of risk management processes and provides independent assurance to the board.
- Employees: All employees should be aware of the risk management policies and practices relevant to their roles in the organization.
Fostering a Risk-Aware Culture Among Employees
Cultivating a risk-aware culture is vital for ensuring that all organizational members recognize and prioritize risk management in their day-to-day activities. This culture fosters an environment where employees feel empowered to identify risks and participate in mitigation efforts.To promote a risk-aware culture, organizations can consider the following actionable tips:
“A proactive approach to risk management involves engaging all employees, not just management.”
- Provide Training: Implement regular training sessions that educate employees about financial risks and the organization’s risk management policies.
- Encourage Open Communication: Establish channels for employees to report risks or concerns without fear of repercussions, fostering a transparent environment.
- Incorporate Risk Management into Performance Metrics: Include risk management performance as a criterion in employee evaluations to emphasize its importance.
- Share Success Stories: Highlight instances where effective risk management led to positive outcomes, reinforcing the value of vigilance.
- Lead by Example: Management should demonstrate commitment to risk management by prioritizing it in strategic discussions and decisions.
Case Studies on Successful Financial Risk Management Practices
In the realm of financial risk management, numerous organizations have showcased exemplary practices that not only mitigated risks but also enhanced their overall performance. These case studies provide valuable insights into effective strategies and the lessons learned from both successful and failed initiatives. Understanding these examples can guide other organizations in refining their own risk management frameworks.The following section highlights notable case studies that illustrate how companies have successfully navigated financial risks.
It emphasizes the methodologies adopted, the outcomes achieved, and the significant lessons that emerged from various industries.
Case Study: JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase implemented a robust financial risk management strategy following the 2008 financial crisis. They focused on enhancing their risk assessment and management frameworks, integrating advanced technology for real-time monitoring and analytics.Key takeaways from JPMorgan Chase’s approach include:
-
Emphasis on a strong risk culture throughout the organization.
-
Investment in technology to improve data analytics capabilities.
-
Regular stress testing to assess potential vulnerabilities.
Case Study: Procter & Gamble
Procter & Gamble adopted a comprehensive risk management strategy that emphasized currency risk management due to its global operations. By utilizing hedging strategies, the company successfully minimized the impact of currency fluctuations.Key takeaways from Procter & Gamble’s experience include:
-
Utilization of hedging strategies to protect against currency volatility.
-
Collaborative approach between finance and operational teams for better risk identification.
-
Continuous monitoring and adjustment of risk management strategies.
Case Study: Boeing, Financial risk management
Boeing faced significant financial risks during the development of its 787 Dreamliner. The company encountered budget overruns and delivery delays, prompting a reevaluation of its risk management practices. Boeing implemented stringent project management controls and improved supplier relationships to mitigate future risks.Key takeaways from Boeing’s initiative include:
-
Importance of robust project management protocols.
-
Building strong supplier partnerships to enhance supply chain resilience.
-
Adapting risk management processes based on project feedback.
Case Study: Barclays
Barclays implemented a novel approach to risk management by integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into its risk assessment frameworks. This has positioned the bank as a leader in sustainable finance, allowing it to identify and mitigate risks associated with environmental changes.Key takeaways from Barclays’ approach include:
-
Incorporation of ESG factors into traditional financial risk models.
-
Proactive engagement with stakeholders regarding risk management practices.
-
Continuous development of risk management strategies that align with global sustainability goals.
Lessons from Failures: Lehman Brothers
The collapse of Lehman Brothers serves as a poignant reminder of the critical importance of effective risk management. The firm failed to adequately assess the risks associated with subprime mortgages, leading to its downfall.Key takeaways from the Lehman Brothers case include:
-
Neglecting to account for systemic risks can lead to catastrophic failures.
-
Overreliance on complex financial instruments without proper oversight can exacerbate risk exposure.
-
Strong governance and risk assessment frameworks are essential for sustainability.
Summary of Key Takeaways
The following table provides a concise overview of the key insights derived from the case studies presented:
| Organization | Key Strategies | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|
| JPMorgan Chase | Risk culture, technology investment, stress testing | Culture and technology are pivotal in risk management. |
| Procter & Gamble | Hedging, collaborative approach, continuous monitoring | Proactive currency management can mitigate financial impacts. |
| Boeing | Project management, supplier partnerships, feedback adaptation | Strong management and supplier relationships are crucial. |
| Barclays | ESG incorporation, stakeholder engagement, sustainable strategy | Integrating ESG factors enhances risk management. |
| Lehman Brothers | Neglect of systemic risks | Overreliance on complexity without oversight leads to failure. |
The Future of Financial Risk Management
The landscape of financial risk management is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and the dynamics of global markets. As firms adapt to these shifts, the focus will increasingly be on creating more robust frameworks that not only mitigate risks but also capitalize on emerging opportunities.The field of financial risk management is witnessing several emerging trends that are reshaping the way organizations approach risk.
Regulatory changes, such as those stemming from the Basel III framework, are influencing capital adequacy and liquidity requirements, compelling institutions to rethink their risk profiles. Additionally, evolving market conditions—spurred by geopolitical uncertainties, climate change, and digital transformation—are creating a more complex risk environment.
Emerging Trends and Future Challenges in Financial Risk Management
The anticipated challenges and opportunities in financial risk management are multifaceted. Organizations will need to stay ahead of regulatory requirements while also adapting to new market realities. Significant changes in consumer behavior, technological advancements, and the rise of sustainable finance will also play crucial roles in shaping future strategies.As we look ahead, several key predictions Artikel how financial risk management practices will evolve over the next decade:
- Increased Automation: The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning will enhance predictive analytics, allowing organizations to identify and respond to risks more swiftly.
- Enhanced Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulators will continue to impose stricter compliance requirements, particularly in the areas of risk disclosure and stress testing, pushing firms to adopt more transparent practices.
- Focus on ESG Risks: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors will become a critical component of risk assessments, with investors increasingly prioritizing sustainable practices.
- Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Concerns: As digital transactions increase, so will the focus on cybersecurity risks, necessitating stronger protective measures and response protocols.
- Integration of Risk and Strategy: Risk management will increasingly be seen as a strategic function, where risk assessments directly inform business decisions and long-term planning.
- Collaboration Across Sectors: Increased collaboration between financial institutions and technology firms will drive innovation in risk management solutions.
The future of financial risk management is poised to be dynamic and complex, presenting both challenges and opportunities for organizations willing to adapt and innovate. The ability to navigate this evolving landscape will determine the resilience and sustainability of financial institutions in the coming years.
Final Wrap-Up
In summary, financial risk management is a crucial aspect of modern business strategy that requires a comprehensive understanding of its principles and practices. By integrating quantitative techniques and embracing technology, organizations can not only identify and manage risks more effectively but also position themselves to seize future opportunities. The evolving landscape of financial risk management calls for continuous adaptation and learning, ensuring that businesses remain resilient in an ever-changing environment.
FAQ Explained: Financial Risk Management
What is financial risk management?
Financial risk management involves assessing and mitigating potential financial losses that an organization may face due to various risks.
Why is financial risk management important?
It helps organizations protect their assets, ensure stability, and make informed decisions, ultimately leading to sustainable growth.
What are the main types of financial risks?
The main types include market risk, credit risk, operational risk, and liquidity risk, each with unique characteristics and impacts.
How can technology improve financial risk management?
Technology enhances risk management through advanced analytics, real-time monitoring, and automated reporting, increasing efficiency and accuracy.
What role do regulatory frameworks play in financial risk management?
Regulatory frameworks provide guidelines and standards that organizations must follow to ensure effective risk management practices, promoting transparency and stability.
What is Value at Risk (VaR)?
Value at Risk (VaR) is a quantitative measure used to assess the potential loss in value of an asset or portfolio over a defined period for a given confidence interval.
How can organizations create a risk-aware culture?
Organizations can foster a risk-aware culture by providing training, encouraging open communication, and integrating risk management into daily operations.