Financial forecasting is a fundamental aspect of strategic business planning that helps organizations predict future financial performance based on historical data and market trends. This intriguing process not only employs various methodologies but also adapts to technological advancements and economic indicators, making it a critical tool for informed decision-making. As businesses navigate through uncertainties, understanding the nuances of financial forecasting can empower them to anticipate changes and optimize their financial strategies.
From traditional methods to modern technological tools, financial forecasting encompasses a range of techniques designed to enhance accuracy and reliability. Companies leverage these methodologies to create actionable insights, assess risks, and align their operational goals with financial realities. This overview will delve into the different methodologies, the influence of technology, and the significance of economic indicators in crafting effective financial forecasts.
Financial forecasting methodologies are critical for businesses and require an understanding of various techniques.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, effective financial forecasting is essential for strategic planning and decision-making. Companies rely on various methodologies to project future financial performance, ensuring that they can allocate resources efficiently, manage risks, and seize opportunities. Understanding these methodologies helps businesses tailor their approaches to meet specific needs and circumstances.Financial forecasting methodologies vary in their approach, each with unique advantages and disadvantages.
Businesses often choose a method based on factors such as the type of data available, the forecasting horizon, and the specific objectives of the forecast.
Common Financial Forecasting Methodologies
Several key methodologies are widely used in financial forecasting, each serving different business needs. Below are some of the most common methods, along with their effectiveness, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
- Quantitative Forecasting
“Quantitative forecasting relies on historical data to make predictions about future financial performance.”
This method uses statistical techniques and mathematical models to predict future outcomes based on past data. It’s particularly effective for businesses with extensive historical records. For instance, a retail company may analyze sales data from previous years to forecast future sales during holiday seasons.
- Advantages: Highly accurate when sufficient historical data is available, allows for automated forecasting, and enables trend analysis.
- Disadvantages: May fail in unprecedented situations, relies heavily on the quality of historical data, and can be complex to implement.
- Qualitative Forecasting
“Qualitative forecasting is based on expert opinions and market research, making it ideal for new or rapidly changing markets.”
This methodology involves subjective judgment rather than statistical analysis. It’s particularly useful for startups lacking sufficient historical data. For example, a tech startup might conduct surveys and interviews to gauge consumer interest in a new product.
- Advantages: Useful for new products or markets, incorporates the expertise of industry professionals, and adapts quickly to changing conditions.
- Disadvantages: Less reliable due to subjectivity, prone to bias, and results can vary significantly based on the experts consulted.
- Time Series Analysis
“Time series analysis examines data points collected or recorded at specific time intervals.”
This method involves analyzing data over time to forecast future trends. A common application is in stock market analysis, where financial analysts use historical price movements to predict future stock performance.
- Advantages: Effective for short-term forecasts, captures seasonal trends and cycles, and often provides clear visualizations of trends.
- Disadvantages: Limited in long-term forecasting, relies on past patterns that may not repeat, and requires significant data to yield reliable forecasts.
- Regression Analysis
“Regression analysis identifies relationships between variables, allowing for accurate predictions based on influencing factors.”
This technique assesses the relationships between dependent and independent variables to forecast outcomes. For example, a car manufacturer could use regression analysis to predict sales based on economic indicators like unemployment rates and consumer confidence indices.
- Advantages: Highlights key factors affecting outcomes, allows for scenario analysis, and can accommodate complex relationships between variables.
- Disadvantages: Requires a strong understanding of statistics, potential for overfitting, and sensitive to outliers that can skew results.
The choice of financial forecasting methodology should align with the specific business context, data availability, and strategic goals. Understanding each method’s strengths and weaknesses enables businesses to craft a forecasting approach that enhances decision-making and drives successful outcomes.
The role of technology in enhancing financial forecasting accuracy should not be underestimated.
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping the landscape of financial forecasting, allowing organizations to make more informed and timely decisions. As businesses navigate increasingly volatile markets, the integration of sophisticated tools and data analytics has become crucial in achieving accuracy and reliability in forecasts.The transformation brought about by technology in financial forecasting processes can be seen through the utilization of various software and analytical tools.
These innovations allow for the aggregation of vast amounts of data, real-time analysis, and predictive modeling, ultimately enhancing the precision of forecasts. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence, organizations can identify trends and patterns that were once difficult to discern, leading to more accurate predictions.
Key tools and software in financial forecasting
The financial forecasting industry has witnessed the emergence of several tools and software that enhance forecasting accuracy. Understanding these tools and their features can provide insight into how organizations effectively integrate technology into their forecasting practices. Some prominent tools include:
- Tableau: A leading data visualization tool that helps companies create interactive and shareable dashboards. It enables users to visualize historical and predictive data, enhancing understanding and decision-making.
- Microsoft Excel: A traditional yet powerful tool for financial forecasting, Excel offers advanced functions and formulas that allow financial analysts to build complex financial models and forecast scenarios.
- Adaptive Insights: A cloud-based financial planning and analysis tool that provides robust forecasting capabilities. Its features include driver-based modeling and real-time collaboration, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Oracle Hyperion: A comprehensive suite for enterprise performance management that includes budgeting, forecasting, and reporting functionalities. It allows organizations to create detailed financial models and analyze their performance against forecasts.
- SAS Forecast Server: A specialized tool designed for advanced forecasting, utilizing statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms to deliver accurate predictions based on historical data.
The impact of these technologies is evident through various case studies. For instance, a multinational retail corporation adopted machine learning algorithms within its forecasting models, resulting in a 20% increase in forecast accuracy over previous methodologies. This improvement allowed the company to optimize inventory levels, reducing excess stock and associated carrying costs. Another example includes a financial services firm that integrated cloud-based analytics into its forecasting process; this shift led to a significant reduction in the time taken to generate forecasts while simultaneously enhancing overall accuracy.In summary, the integration of technology in financial forecasting is not merely an enhancement but a necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s data-driven environment.
Leveraging sophisticated tools and methodologies can lead to improved accuracy, efficiency, and ultimately, better strategic decision-making.
Understanding the impact of economic indicators on financial forecasting is essential for informed decision-making.
Economic indicators offer critical insights that shape financial forecasts and guide strategic decision-making. By analyzing these indicators, businesses can gain a clearer understanding of market trends, consumer behavior, and economic stability. This understanding ultimately enables organizations to make informed decisions about investments, resource allocation, and risk management.Economic indicators can be categorized into three main types: leading, lagging, and coincident indicators.
Each type offers unique insights into different stages of the economic cycle. Leading indicators, such as consumer sentiment and stock market performance, signal future economic activity. Lagging indicators, such as unemployment rates and GDP growth, provide insight into past economic performance. Coincident indicators, like retail sales, reflect the current state of the economy.
Key Economic Indicators and Their Relevance, Financial forecasting
Understanding the most significant economic indicators is vital for accurate financial forecasting. Below is a table illustrating key economic indicators and their correlation with forecast outcomes:
| Economic Indicator | Type | Correlation with Forecast Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | Lagging | Indicates overall economic health; higher GDP correlates with positive financial forecasts. |
| Unemployment Rate | Lagging | High unemployment may predict lower consumer spending, negatively impacting forecasts. |
| Consumer Price Index (CPI) | Lagging | Rising CPI indicates inflation, which can lead to increased costs and reduced profit forecasts. |
| Stock Market Performance | Leading | A rising stock market often predicts increased economic activity and higher forecasts. |
| Retail Sales | Coincident | Increased retail sales indicate strong consumer demand, positively influencing financial projections. |
| Manufacturing Index | Leading | A rising index suggests future economic growth, improving overall forecast accuracy. |
Incorporating these economic indicators into forecasting models is essential for enhancing accuracy and reliability. Various methods can be employed:
1. Regression Analysis
This statistical method helps in determining the relationship between economic indicators and forecast outcomes. By using historical data, regression models can predict future trends based on changes in indicators.
2. Scenario Analysis
This technique involves creating different economic scenarios based on potential changes in key indicators. It helps organizations prepare for various outcomes and adjust their forecasts accordingly.
3. Time Series Analysis
By analyzing historical data points, organizations can identify trends and patterns associated with economic indicators, facilitating more precise financial forecasting.
4. Expert Judgment
Engaging industry experts to interpret economic indicators can provide qualitative insights that enhance quantitative forecasts, ensuring a more well-rounded approach.Incorporating these techniques effectively positions organizations to navigate economic fluctuations while making informed financial decisions that align with market realities.
The significance of scenario planning in financial forecasting cannot be ignored.
Scenario planning plays a critical role in financial forecasting by allowing organizations to explore and prepare for various potential futures. It involves creating detailed narratives or models that represent different possibilities based on varying economic conditions, regulatory changes, or market trends. This approach not only enhances the accuracy of forecasts but also equips businesses with the agility to navigate uncertainties in a rapidly changing environment.Scenario planning enables organizations to visualize diverse financial outcomes, which can be pivotal for strategic decision-making.
By considering multiple scenarios, businesses can develop a more robust understanding of risks and opportunities associated with each potential future. This proactive approach aids in identifying key drivers of change and helps organizations formulate appropriate strategies.
Techniques for developing financial scenarios based on varying assumptions
In developing financial scenarios, it is essential to apply systematic techniques that allow for comprehensive analysis. The following methods are effective in creating diverse scenarios:
- Trend Analysis: This technique involves examining historical data to identify patterns and project future trends. Businesses can leverage statistical methods to create projections based on past performance, considering both linear and non-linear trends.
- What-If Analysis: This method allows organizations to test various assumptions by altering specific variables, such as interest rates or market demand. By evaluating the impact of these changes on financial outcomes, companies can gauge potential risks and rewards.
- Cross-Impact Analysis: This technique examines how different variables may influence one another. By understanding interdependencies, organizations can better assess how changes in one area might affect overall financial performance.
- Expert Judgement: Engaging industry experts to provide insights on potential future developments can enhance scenario planning. Their knowledge can guide the creation of realistic and relevant scenarios based on current market dynamics.
The integration of these techniques ensures a well-rounded approach to scenario planning, enabling businesses to create comprehensive models that can inform strategic choices.
Implications of scenario planning for risk management and strategic decision-making
Scenario planning significantly impacts an organization’s risk management strategy. By anticipating various potential futures, businesses can identify vulnerabilities and devise mitigation strategies before challenges arise. This foresight helps in safeguarding assets and ensuring operational continuity.Moreover, scenario planning enhances strategic decision-making by providing a framework for evaluating options against different potential futures. Decision-makers can weigh the consequences of their choices based on diverse scenarios, leading to more informed and strategic outcomes.
The ability to visualize multiple futures enables organizations to remain agile and responsive, turning uncertainty into opportunity.
Organizations that embrace scenario planning can foster a culture of adaptability. This approach not only prepares them for adverse conditions but also positions them to capitalize on emerging trends and opportunities that may arise in the marketplace. As a result, scenario planning becomes an invaluable tool in steering financial forecasting and strategic initiatives toward sustainable growth.
Evaluating the accuracy of financial forecasts plays a crucial role in refining future predictions.
In the financial realm, the precision of forecasts can significantly influence decision-making processes and strategic planning. Evaluating the accuracy of these financial predictions not only helps organizations to improve their forecasting techniques but also instills confidence among stakeholders. Understanding how to measure this accuracy is vital for continuous improvement and alignment with market dynamics.Assessing the accuracy of financial forecasts involves various metrics, each providing insights into different aspects of prediction quality.
These metrics serve as benchmarks for organizations to evaluate their forecasting performance, leading to better outcomes in future predictions. Some widely used metrics include:
Metrics for assessing accuracy
The effectiveness of financial forecasting can be quantified through several key metrics. Each metric sheds light on different facets of forecast performance.
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE): This metric measures the average magnitude of the errors in a set of forecasts, without considering their direction. The formula is:
MAE = (1/n)
– Σ |Forecast – Actual|A lower MAE indicates more accurate forecasts.
- Mean Squared Error (MSE): This calculates the average of the squares of the errors, emphasizing larger discrepancies. The formula is:
MSE = (1/n)
– Σ (Forecast – Actual)²MSE is useful in assessing the variance of forecast errors.
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): RMSE is the square root of MSE and provides a measure of the average error magnitude in the same unit as the forecast. The formula is:
RMSE = √MSE
It is often used for comparing forecasting models.
- Tracking Signal: This is a metric that indicates whether a forecasting model is consistently over or under-predicting. A tracking signal outside the range of -4 to +4 typically indicates a need for model adjustment.
- Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): MAPE expresses accuracy as a percentage, making it easier to understand. The formula is:
MAPE = (100/n)
– Σ |(Forecast – Actual) / Actual|This metric is particularly useful when comparing forecast accuracy across different scales.
Integrating feedback loops into the forecasting process is essential for enhancing accuracy over time. Feedback loops involve continuously collecting data on forecast performance, analyzing the discrepancies, and refining forecasting methods accordingly. This iterative process fosters a culture of learning and adaptation, allowing organizations to adjust their strategies based on real-world outcomes.
Importance of feedback loops
Feedback loops create opportunities for organizations to learn from past forecasting errors and successes. By systematically reviewing forecast performance and implementing changes, businesses can significantly improve their forecasting accuracy.For instance, a well-known retail chain, Target, leverages feedback loops by analyzing sales data and customer behavior to refine their inventory forecasts. When discrepancies arise, Target reviews the underlying assumptions and model inputs, making necessary adjustments to their forecasting techniques.
As a result, they have achieved greater accuracy in predicting product demand, minimizing stockouts and excess inventory.Another example can be seen in the technology sector with companies like Apple. Apple’s forecasting team regularly evaluates sales data against their projections, enabling them to refine their production schedules for new product launches. By employing a feedback loop, they have managed to optimize their supply chain processes and reduce lead times, ultimately leading to better alignment with consumer demand.Through the implementation of robust metrics and effective feedback mechanisms, organizations can create a cycle of continuous improvement that enhances the accuracy of their financial forecasts.
This proactive approach not only optimizes operational efficiency but also boosts stakeholder confidence in financial planning and strategy execution.
The challenges faced in financial forecasting must be addressed to enhance predictability.
Financial forecasting plays a crucial role in the strategic planning of any organization. However, it is often riddled with challenges that can significantly undermine the accuracy and reliability of predictions. Addressing these obstacles is essential for enhancing predictability and ensuring that organizations can make informed decisions based on solid financial insights.One of the primary obstacles organizations face in financial forecasting is the unpredictability of external factors such as economic conditions, regulatory changes, and market volatility.
These uncertainties can lead to significant deviations between forecasts and actual performance, impacting the organization’s ability to allocate resources effectively. Moreover, internal factors like inefficient data management processes, lack of historical data, and inadequate analytical tools further complicate the forecasting landscape.
Common obstacles in financial forecasting
To understand the challenges more clearly, here are some common obstacles that organizations encounter:
- External market volatility – Fluctuations in the market can create unpredictable changes that affect financial forecasts.
- Data quality issues – Inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated data can lead to poor forecasting accuracy.
- Resource constraints – Limited financial and human resources can hinder the forecasting process.
- Lack of collaboration – Insufficient communication between departments can lead to fragmented forecasts that don’t align with organizational goals.
- Over-reliance on historical data – Solely depending on past data without adjusting for current trends can skew forecasts.
These challenges not only affect the forecasting outcome but can also have detrimental effects on the overall business strategy and performance. For instance, a company that fails to account for market volatility may overestimate revenues, leading to misallocation of resources and potential cash flow issues.
Strategies for overcoming forecasting challenges
Organizations can implement several strategies to overcome these forecasting hurdles and enhance predictability. Here are some effective approaches:
- Invest in advanced analytical tools – Utilizing modern forecasting software can improve data accuracy and streamline the forecasting process.
- Foster interdepartmental collaboration – Encouraging communication between finance, sales, and operations ensures that forecasts are comprehensive and aligned with overall business objectives.
- Allocate sufficient resources – Ensuring that the forecasting team is adequately staffed and supported can improve both the quality and speed of forecasts.
- Regularly update models – Continually revising forecasting models to reflect new data and trends can help maintain their relevance and accuracy.
- Conduct scenario analysis – Utilizing scenario planning can help organizations prepare for various potential market conditions and their impacts on forecasts.
Examples of successful forecasting navigation
Several companies have successfully navigated the challenges of financial forecasting, providing valuable lessons for others. For example, Coca-Cola has implemented advanced analytics and machine learning to enhance its forecasting capabilities. By integrating data from multiple sources and continuously refining their predictive models, they have improved their inventory management and reduced wastage.Another notable example is Unilever, which utilizes collaborative forecasting techniques across its global teams.
By promoting communication and data sharing, Unilever has achieved more accurate demand forecasts, allowing for better resource allocation and inventory management.These examples demonstrate that addressing the challenges in financial forecasting is not only possible but can also lead to significant operational improvements and business success. The key takeaway is that organizations must invest in technology, foster collaboration, and remain adaptable to changing market conditions in order to enhance their forecasting predictability.
Collaboration across departments can significantly enhance the financial forecasting process.
The intricacies of financial forecasting necessitate a concerted effort across various departments. When teams such as finance, marketing, sales, and operations collaborate, they can create a more accurate and comprehensive financial forecast. This cross-functional synergy not only streamlines data collection but also enriches the forecasting process by integrating diverse viewpoints and expertise.Effective financial forecasting relies on the unique contributions of different departments.
Each team provides critical insights that form the bedrock of accurate predictions. For instance, the sales department offers data on anticipated sales volumes and market trends, while the marketing team shares insights on forthcoming campaigns that could influence revenue. Operations can provide information on production capacity and cost structures, ensuring that forecasts account for potential supply chain constraints.
Strategies for fostering collaboration and communication among teams
Establishing a culture of collaboration is essential for improving the forecasting process. Here are several effective strategies to enhance interdepartmental communication and cooperation:
Regular Cross-Departmental Meetings
Schedule consistent meetings where representatives from each department can share relevant updates and insights. This creates a platform for discussing challenges and aligning forecasts with real-time data.
Use of Collaborative Tools
Implement cloud-based software that allows teams to update and share financial data seamlessly. Tools such as Google Workspace, Microsoft Teams, or specialized financial forecasting platforms can facilitate real-time collaboration and ensure everyone is on the same page.
Shared Goals and Metrics
Establish common objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) that all departments can work towards. This encourages a unified approach to forecasting as everyone understands how their contributions affect overall financial performance.
Cross-Functional Training
Encourage team members to participate in workshops or training sessions conducted by other departments. This not only increases understanding of each team’s role but also fosters empathy and improves communication across divisions.
Feedback Mechanisms
Create structured feedback loops where team members can provide input on forecasts and processes. This helps identify any discrepancies or areas for improvement, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability among all departments involved.By leveraging the strengths of each department, organizations can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of their financial forecasts. A collaborative approach not only leads to better predictions but also fosters a more cohesive organizational culture, ultimately driving improved business outcomes.
Ethical considerations in financial forecasting are vital for maintaining integrity and trust.

In the realm of finance, ethical considerations hold paramount significance as they directly impact the integrity and trustworthiness of financial forecasting. Stakeholders, including investors, clients, and regulatory bodies, depend on accurate and ethically-sound forecasts to make informed decisions. The absence of ethical standards can lead to misrepresentation of data, manipulation of forecasts, and ultimately, a loss of trust in financial institutions.Ethical implications arise throughout the financial forecasting process, as various factors can influence the objectivity and accuracy of predictions.
These factors include the pressure to meet expectations, conflicts of interest, and the potential for bias in modeling assumptions. Consequently, financial professionals must navigate these complexities while adhering to ethical guidelines to uphold the credibility of their forecasts.
Examples of Ethical Dilemmas in Financial Forecasting
Financial forecasting can present ethical dilemmas that challenge the integrity of the forecasting process. Understanding and addressing these dilemmas is crucial for maintaining trust in financial practices. Some common examples of these dilemmas include:
- Pressure to Inflate Projections: Financial analysts may face pressure to provide overly optimistic forecasts to please stakeholders or secure funding. This can lead to inflated projections that mislead investors.
- Conflict of Interest: When analysts are incentivized based on the performance of certain assets, they may exhibit bias in their forecasts, compromising their objectivity.
- Selective Disclosure: Withholding unfavorable information or selectively presenting data can distort the true financial picture, undermining transparency.
- Manipulation of Assumptions: Altering key assumptions in financial models to achieve desired results can lead to unethical forecasting practices.
To address these dilemmas, financial professionals can adopt a code of ethics that emphasizes objectivity, honesty, and transparency. Regular training sessions and open discussions about ethical practices can also foster a culture of integrity within financial institutions.
Importance of Transparency and Accountability in Financial Forecasting Practices
Transparency and accountability are critical components of ethical financial forecasting. These principles ensure that stakeholders have access to the necessary information to make informed decisions. Transparency involves not only accurate reporting of forecasts but also the clear communication of the methodologies and assumptions behind those forecasts.Providing detailed insight into the forecasting process enhances credibility and allows stakeholders to understand the basis of projections.
This openness can prevent potential disputes or misunderstandings regarding the financial outlook.Accountability plays a vital role in maintaining ethical standards. Financial forecasters must be held responsible for their predictions and the methodologies used. Establishing a framework for regular audits and peer reviews can help ensure that forecasts adhere to ethical guidelines and best practices.In summary, the ethical considerations in financial forecasting are not merely guidelines but essential practices that uphold integrity and trust in the financial industry.
By addressing ethical dilemmas and fostering transparency and accountability, financial professionals can contribute to a more trustworthy forecasting environment.
End of Discussion
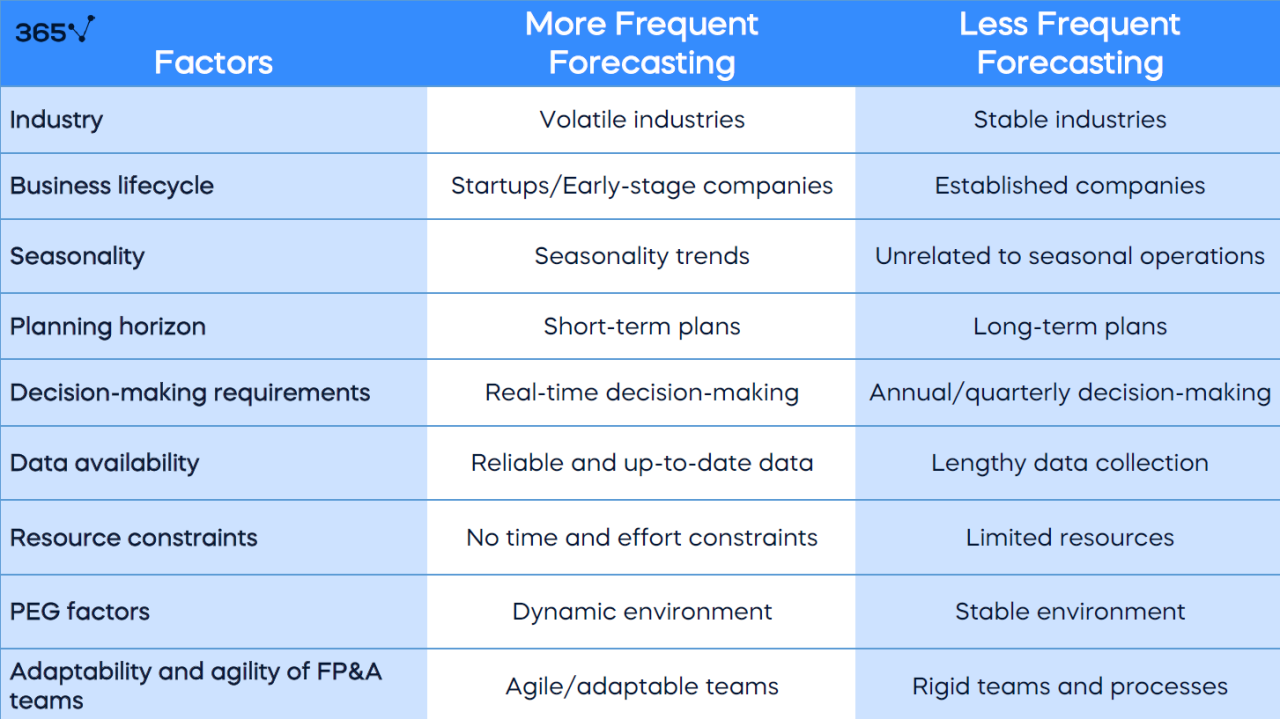
In summary, mastering financial forecasting is essential for businesses striving to achieve greater financial stability and growth. By exploring various methodologies, incorporating technology, and understanding economic impacts, companies can refine their forecasting skills to navigate future uncertainties more effectively. Ultimately, the ability to create accurate forecasts can serve as a competitive advantage, fostering resilience and adaptability in an ever-changing market environment.
Common Queries
What is financial forecasting?
Financial forecasting is the process of estimating future financial outcomes based on historical data, trends, and assumptions.
Why is financial forecasting important?
It helps businesses make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and plan for future growth or challenges.
What methodologies are commonly used in financial forecasting?
Common methodologies include quantitative methods, qualitative methods, time series analysis, and regression analysis.
How does technology improve financial forecasting?
Technology enhances forecasting accuracy through advanced software tools that automate data analysis and modeling processes.
What role do economic indicators play in financial forecasting?
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into market conditions, helping businesses adjust their forecasts based on economic trends.
What is scenario planning in financial forecasting?
Scenario planning involves creating different financial scenarios based on varying assumptions to prepare for various potential futures.
How can businesses evaluate the accuracy of their forecasts?
Businesses can use metrics such as mean absolute error (MAE) and root mean square error (RMSE) to assess forecast accuracy.
What challenges do organizations face in financial forecasting?
Common challenges include data quality issues, changing market conditions, and lack of collaboration among departments.
How can ethical considerations affect financial forecasting?
Ethical considerations ensure transparency and accountability in financial forecasting practices, maintaining trust with stakeholders.