Mortgage rates are a crucial component for anyone looking to buy a home or refinance an existing loan. Understanding how these rates work, what influences them, and the different types available can empower borrowers to make informed decisions. From fixed rates to adjustable rates, this exploration will unravel the complexities of mortgage rates and offer insights that can lead to significant savings.
As we dive deeper, we will examine the fundamental aspects of mortgage rates, including how they are set by lenders and the economic indicators that play a pivotal role in shaping these rates. Armed with this knowledge, borrowers will be better equipped to navigate the housing market and secure favorable loan terms.
Understanding the Basics of Mortgage Rates
Mortgage rates are a crucial component of home financing, affecting how much you will pay over the life of your loan. Essentially, a mortgage rate is the interest charged on a mortgage, expressed as a percentage of the total loan amount. This rate can either be fixed, where the interest rate remains constant throughout the life of the loan, or adjustable, where the rate fluctuates based on market conditions.
Understanding the different types of mortgage rates is essential for potential borrowers, as these rates directly impact monthly payments and the overall cost of purchasing a home.Fixed-rate mortgages are typically favored by those who prefer stability in their financial planning. These rates remain unchanged, providing predictability over the years. In contrast, adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) start with lower initial rates that can increase or decrease at specified intervals, depending on the market.
This means borrowers could benefit from lower payments initially but face the possibility of increased costs down the line. Additionally, there are hybrid options, which combine elements of both fixed and adjustable rates. By understanding these basic concepts, homebuyers can make informed decisions about their mortgage options.
Factors Influencing Mortgage Rates
Numerous factors affect mortgage rates in the market, and understanding these influences can empower borrowers to secure the best possible rate. The primary elements include economic indicators, the Federal Reserve’s actions, and individual borrower profiles.Economic indicators such as inflation, employment rates, and GDP growth play a significant role in determining interest rates. Generally, when the economy is strong, inflation rises, leading to higher mortgage rates.
Conversely, during economic downturns, rates may decrease to stimulate borrowing and spending. The Federal Reserve (often referred to as the Fed) also significantly impacts mortgage rates through its monetary policy. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money, leading to higher mortgage rates for consumers. Additionally, individual borrower profiles, including credit scores, loan amounts, and down payment sizes, can influence the rates that lenders offer.
Higher credit scores generally result in better rates, as they signal to lenders that borrowers are less likely to default on their loans.
Setting Mortgage Rates by Lenders
Mortgage rates are set by lenders based on a combination of market conditions, perceived risk, and operational costs. Lenders consider the current economic environment, including supply and demand for loans, when determining their rates. If demand for mortgages is high, lenders may increase rates to maximize profit. Conversely, in a saturated market with many available loans, rates may drop to attract borrowers.Lenders also evaluate the risk associated with the loan they are extending.
A borrower with a lower credit score is viewed as a higher risk compared to someone with a stellar credit history. To compensate for this risk, lenders may charge higher interest rates to ensure they cover potential losses. Operational costs, including underwriting, servicing, and maintaining the mortgage, also play a significant role in setting rates. Lenders need to ensure that their rates not only attract borrowers but also cover these costs and provide a profit margin.
In summary, mortgage rates are influenced by a confluence of economic factors, borrower profiles, and lender strategies. Understanding these elements can help borrowers navigate the mortgage landscape more effectively.
The Impact of Economic Indicators on Mortgage Rates
Understanding the various economic indicators that influence mortgage rates is crucial for borrowers who aim to make informed financial decisions. These indicators provide insights into the overall economic health, which directly correlates with the cost of borrowing money for home purchases. Among these indicators, inflation and the actions of the Federal Reserve play significant roles in shaping mortgage rates, affecting affordability and loan conditions for borrowers.
Inflation and Its Effects on Mortgage Rates
Inflation is a key economic indicator that significantly impacts mortgage rates. As inflation rises, the purchasing power of money decreases, driving lenders to raise interest rates to compensate for the decreased value of future repayments. This means that borrowers end up paying more for loans in real terms. Lenders are particularly sensitive to inflation because it erodes the returns on fixed-rate loans; thus, higher inflation typically leads to higher mortgage rates.
For instance, if inflation increases to 5% annually, lenders might respond by raising mortgage rates to ensure they maintain their profit margins. Higher mortgage rates can substantially increase monthly payments, making homeownership less affordable. This relationship between inflation and mortgage rates matters to borrowers, as it directly affects affordability and the overall cost of homeownership. Borrowers need to stay informed about inflation trends because they can influence timing for purchasing a home or refinancing existing loans.
For example, a borrower may decide to lock in a mortgage rate before anticipated inflation spikes, which could lead to higher rates in the future. Additionally, if inflation expectations are moderate, borrowers may benefit from relatively stable or lower rates, allowing for better financial planning and budgeting.
Federal Reserve Interest Rate Decisions and Mortgage Rates
The Federal Reserve plays a pivotal role in determining the direction of mortgage rates through its monetary policy decisions, particularly its federal funds rate. When the Fed raises or lowers this rate, it influences the overall cost of borrowing money across the economy, including mortgage loans. An increase in the federal funds rate often leads to corresponding increases in mortgage rates, making home loans more expensive for consumers.
Conversely, when the Fed lowers rates, it typically results in lower mortgage rates, encouraging borrowing and spending.
For example, during economic downturns, the Fed may reduce interest rates to stimulate growth. In 2008, in response to the financial crisis, the Fed slashed rates to near-zero levels, resulting in historically low mortgage rates that spurred home purchases and refinances. This relationship underlines the importance of the Fed’s decisions for borrowers; understanding the Fed’s policy direction can help borrowers anticipate changes in mortgage rates.
Additionally, the Fed’s announcements and the economic context surrounding them can create volatility in mortgage rates. If the market perceives that the Fed will maintain low rates for an extended period, mortgage rates may remain stable. However, if there are signs of economic recovery or inflationary pressures, the Fed may signal potential rate hikes, leading to increases in mortgage rates.
Therefore, borrowers should closely monitor the Fed’s monetary policy and economic forecasts to gauge when to secure a mortgage.
Key Economic Indicators Predictive of Mortgage Rate Movements
Several economic indicators serve as reliable predictors of mortgage rate movements, providing borrowers with insights into market trends. These include inflation rates, employment statistics, GDP growth, and consumer confidence levels. Each of these factors can influence the decisions made by lenders and the Federal Reserve, ultimately affecting mortgage rates.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is often cited as a primary measure of inflation, indicating how fast prices are rising in the economy. A consistent increase in the CPI signals rising inflation, leading to higher mortgage rates as lenders anticipate costlier loans. Employment statistics also play a crucial role; a robust job market typically suggests economic strength, which can prompt the Fed to raise interest rates, thereby increasing mortgage rates.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth is another important factor. A growing economy generally indicates higher consumer spending and investment, which can lead to inflation and subsequent increases in interest rates. Additionally, consumer confidence metrics help gauge how optimistic consumers feel about the economy, influencing their willingness to take on debt, including mortgages. When confidence is high, demand for housing typically increases, potentially driving up mortgage rates as lenders adjust to the higher demand.
By keeping an eye on these indicators, borrowers can gain a better understanding of potential shifts in mortgage rates, enabling them to make timely and informed decisions regarding their home financing options.
Different Types of Mortgage Rates and Their Implications
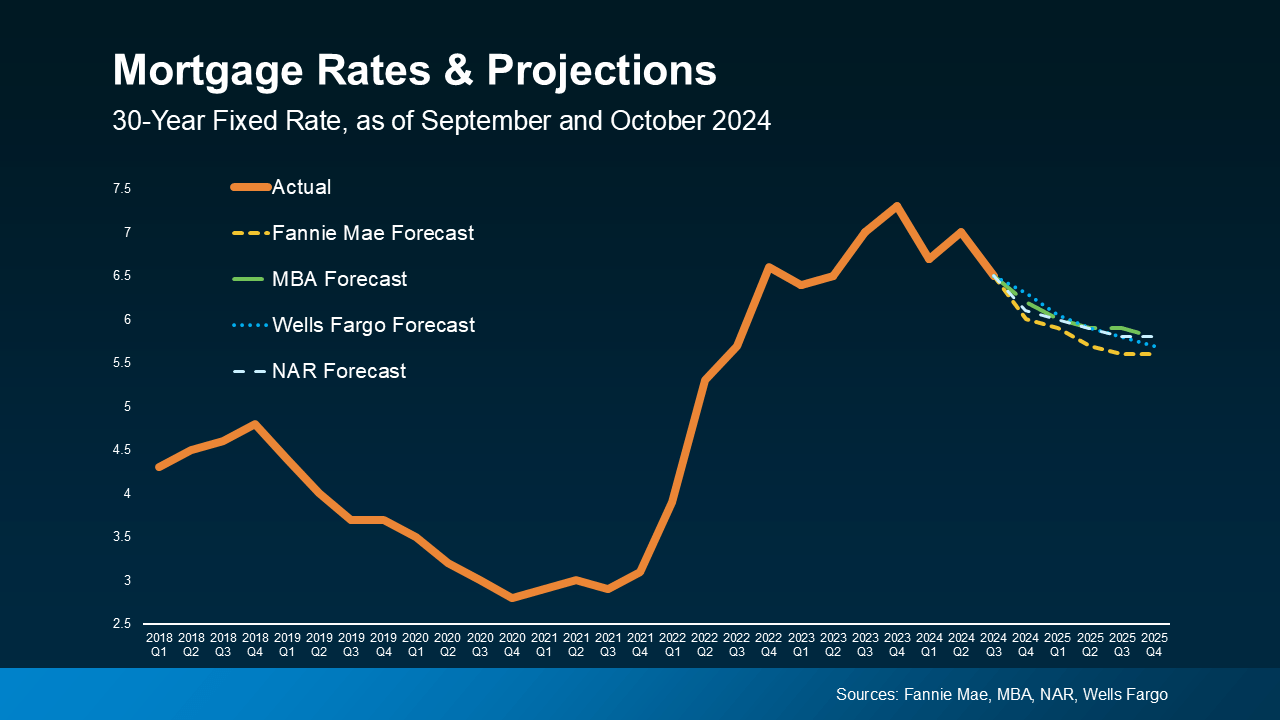
Understanding mortgage rates is crucial for anyone looking to secure a home loan. The choice between different types of mortgage rates can significantly impact monthly payments and overall financial health. This discussion will delve into fixed-rate versus adjustable-rate mortgages, different mortgage programs, and the pros and cons associated with these varying options.
Fixed-Rate versus Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages provide borrowers with a stable interest rate for the entire loan term, which is typically 15, 20, or 30 years. This predictability makes it easier for homeowners to budget their monthly payments. For instance, a homeowner opting for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage at 3.5% will have the same interest rate throughout the life of the loan, regardless of market fluctuations.
This is particularly beneficial in times of rising interest rates, as the borrower is shielded from increases.Conversely, adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) start with a lower initial interest rate that can change after a specified period, often resulting in lower initial payments. For example, a 5/1 ARM has a fixed rate for the first five years and then adjusts annually based on market conditions.
This can lead to significantly lower payments in the initial years, making it an attractive option for buyers planning to move or refinance within a short timeframe. However, after the initial period, rates can rise, potentially leading to higher monthly payments. For instance, if market rates rise to 5% after the initial period, the homeowner will experience a noticeable increase in their monthly payment.Both types of mortgages have distinct implications.
Fixed-rate mortgages lend stability, while ARMs can offer lower initial payments but come with the risk of future increases. Understanding these nuances is essential for making informed decisions.
Various Mortgage Programs Available
Different mortgage programs cater to a range of buyers, each with unique rates and conditions. Notable programs include FHA loans and VA loans, which are designed to assist specific groups of borrowers.FHA loans are backed by the Federal Housing Administration and are particularly beneficial for first-time homebuyers or those with lower credit scores. These loans typically require a down payment as low as 3.5% and allow for higher debt-to-income ratios.
A typical scenario might involve a borrower with a credit score of 620 needing a loan for a $200,000 home. This borrower could access an FHA loan, making homeownership more attainable despite financial limitations.VA loans are available to veterans, active-duty service members, and certain members of the National Guard and Reserves. These loans offer attractive terms, such as no down payment requirement and no private mortgage insurance (PMI).
For example, a veteran purchasing a home priced at $300,000 can secure a VA loan without needing a down payment, significantly reducing the immediate financial burden.Both FHA and VA loans have specific eligibility requirements and benefits that can ease the homebuying process. Borrowers should evaluate these options to determine the best fit for their financial situation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Mortgage Rate Types
When considering mortgage rate types, it’s essential to weigh their advantages and disadvantages carefully. Fixed-rate mortgages provide consistent monthly payments, making budgeting easier and protecting borrowers from interest rate fluctuations. However, the trade-off is that these rates tend to be higher than the initial rates offered by ARMs, potentially leading to larger payments in the early years.Adjustable-rate mortgages offer lower initial rates that can lead to considerable savings upfront.
They are ideal for those who plan to move or refinance before the rate adjusts. However, the risk lies in the potential for significant payment increases after the initial fixed period, which can strain a household’s budget if rates rise sharply.Additionally, FHA loans present a pathway to homeownership for those with lower credit scores, but they also come with mortgage insurance costs that can increase monthly payments.
VA loans, while advantageous due to their no down payment feature, are limited to qualified veterans and military personnel, making them inaccessible to the general public.In summary, understanding the implications of fixed versus adjustable-rate mortgages, exploring various loan programs, and considering the pros and cons of each option are critical steps in making informed financial decisions when purchasing a home.
Strategies for Securing the Best Mortgage Rates
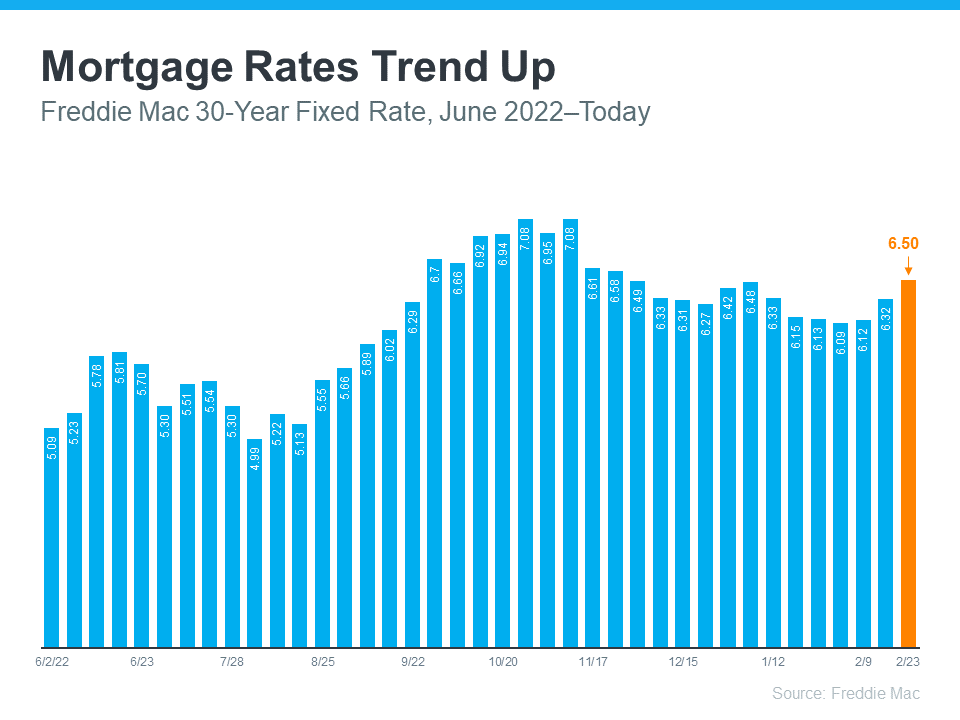
Securing a favorable mortgage rate can significantly impact your financial future, making it crucial to understand effective strategies to improve your position. Borrowers often overlook the importance of their credit scores, timing the market, and gathering necessary documentation. A strategic approach can lead to substantial savings over the life of a loan.
Improving Credit Scores
A higher credit score is one of the most effective ways to secure better mortgage rates. Lenders view credit scores as a reflection of a borrower’s reliability and financial responsibility. Here are some strategies to improve your credit score:
- Pay Bills on Time: Payment history accounts for 35% of your credit score. Consistently paying bills on time can prevent negative marks on your credit report.
- Reduce Credit Card Balances: Aim to keep your credit utilization ratio below 30%. High balances relative to your credit limit can negatively affect your score.
- Avoid New Debt: Each new account opened can lower your average account age and temporarily reduce your score. Avoid applying for new credit cards or loans before applying for a mortgage.
- Check Your Credit Report: Regularly review your credit report for errors. Disputing inaccuracies can help improve your score quickly.
- Limit Hard Inquiries: When you apply for credit, lenders perform inquiries that can impact your score. Try to limit these inquiries, especially before applying for a mortgage.
Timing the Market for Locking in Rates
The timing of locking in a mortgage rate is crucial for maximizing savings. Here are practical tips for borrowers to consider:To effectively time the market, it’s essential to monitor economic indicators such as the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions, inflation rates, and employment data. Historically, mortgage rates tend to rise in response to economic growth and fall during economic downturns.Consider locking in a rate when the market shows signs of upward movement.
If rates begin climbing, a lock can protect you from future increases. On the other hand, if the rates are high, it may be worthwhile to wait for a potential dip. A common strategy is to watch the market for trends over several weeks rather than relying on short-term fluctuations.Additionally, consult with mortgage professionals who can provide insights and guidance regarding the best time to lock in.
They often have access to tools and analytics that predict rate movements based on current market conditions.
Documents Needed for Mortgage Application
When applying for a mortgage, having the correct documentation is essential to streamline the process. It not only demonstrates preparedness but also expedites approval. Below is a list of common documents required:The following documents are typically needed for a mortgage application:
- Proof of Income: Recent pay stubs, W-2 forms, and tax returns for the past two years.
- Credit History: Lenders will pull your credit report, but be ready to explain any discrepancies.
- Asset Statements: Bank statements for the last two months, showing your savings and checking accounts.
- Identification: Government-issued ID (like a passport or driver’s license) along with your Social Security number.
- Debt Information: A list of all debts, including credit cards, student loans, and any other loans.
Having these documents ready can facilitate a smoother application process and help in obtaining the best possible mortgage rates.
The Role of Mortgage Rate Trends in Real Estate Investment
Understanding mortgage rate trends is crucial for real estate investors, as these rates directly impact the affordability of properties and the overall cost of financing. Since mortgage rates fluctuate based on various economic factors, being informed about these trends can help investors make timely and strategic decisions. Investors who track these trends can better assess when to buy, hold, or sell properties, thereby maximizing their returns while minimizing risks.
A keen awareness of mortgage rates not only influences individual investment choices but can also have broader implications for market dynamics.Mortgage rates have experienced significant fluctuations over the past decade, shaping the landscape of real estate investment and ownership. In the early 2010s, post-recession recovery saw rates falling to historic lows, hovering around 3.5% in 2013. This environment encouraged many buyers to enter the market, leading to increased home sales and rising property prices.
As the economy strengthened, the Federal Reserve began to signal a gradual increase in rates, reaching around 4.5% by the end of 2018. This shift prompted buyers to act quickly, fearing further increases and adjusting their expectations regarding affordability.The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 led to another dramatic drop in mortgage rates, with the average 30-year fixed rate falling below 3% for the first time in history.
This scenario created an unprecedented buying frenzy, as low rates attracted both first-time buyers and seasoned investors, consequently driving home prices to record highs. As of late 2022 and into 2023, however, rising inflation concerns and subsequent Fed rate hikes have caused mortgage rates to spike again, reaching over 7% in some instances. This has led to a cooling off in the market, as potential buyers grapple with affordability challenges and adjustable financial expectations.
Consequently, understanding these historical patterns not only aids current buyers in making informed decisions but also prepares investors for future market shifts.Local market conditions play a pivotal role in determining how mortgage rates impact specific areas. Each locality can experience varying economic circumstances, including employment rates, average income levels, and population growth, all of which influence demand for housing and, ultimately, mortgage rates.
In a thriving urban center, for instance, higher demand can sustain elevated property prices, even as mortgage rates fluctuate. Conversely, in rural areas or regions experiencing economic downturns, rising rates may lead to a more pronounced slowdown in property transactions.Furthermore, the presence of local lenders and their respective interest rate offerings can create disparities in mortgage rates across different regions.
For instance, some local banks may provide competitive rates to attract borrowers, while others may adhere to higher rates based on their operational costs or risk assessments. In summary, understanding mortgage rate trends, historical movements, and local market conditions gives real estate investors a comprehensive framework for making informed investment decisions. Recognizing how these elements interplay not only enhances a buyer’s ability to navigate the market but also helps to anticipate future opportunities and challenges.
The Future of Mortgage Rates
The landscape of mortgage rates is continuously evolving, influenced by a myriad of economic indicators, market conditions, and legislative changes. As we look ahead, various insights and predictions from industry experts provide a clearer picture of where mortgage rates may be headed. Understanding these trends can help potential homebuyers and homeowners navigate their financial decisions more effectively.The current economic environment is characterized by inflationary pressures, shifting monetary policy, and a post-pandemic recovery that continues to unfold.
Experts predict that mortgage rates will fluctuate in response to these factors. Analysts from the Mortgage Bankers Association anticipate that rates may stabilize but could remain elevated compared to the historically low levels seen during the pandemic. Current trends suggest a gradual increase in rates as the Federal Reserve aims to control inflation while supporting economic growth.
Impact of Legislation and Economic Shifts on Mortgage Rates
Upcoming legislation and broader economic shifts are critical components that can drastically influence mortgage rates. Legislative changes, particularly those related to housing policy, tax incentives, and consumer protection, can create ripple effects in the mortgage market. For instance, proposed reforms to enhance affordable housing could increase demand, thereby putting upward pressure on rates. Economic shifts such as employment rates, wage growth, and consumer spending also play pivotal roles.
A robust job market typically leads to increased consumer confidence, resulting in higher demand for homes and subsequently higher mortgage rates. Conversely, an economic downturn might lead to decreased demand, potentially lowering rates. The interplay between these factors can be illustrated as follows:
Inflation Control Measures
If the Federal Reserve continues to raise interest rates to combat inflation, borrowing costs, including mortgage rates, are likely to rise.
Legislative Incentives for Homebuyers
Legislative measures aimed at stimulating first-time homebuyer activity could lead to increased competition in the housing market, which may drive rates higher.
Market Volatility
Economic uncertainties, such as geopolitical tensions or unexpected financial crises, can prompt a flight to safety, impacting mortgage-backed securities and influencing rates.As these elements converge, the overall outlook for mortgage rates remains complex and multifaceted.
Scenario-Based Forecast of Mortgage Rates
Forecasting mortgage rates across different economic scenarios provides valuable insights for prospective homeowners. Here are a few plausible scenarios:
1. Economic Growth Scenario
If the economy continues to grow robustly with low unemployment and rising wages, mortgage rates could rise to around 6.5% to 7.0%. This would be driven by increased consumer demand for housing coupled with tighter monetary policy.
2. Recession Scenario
In the event of a recession, characterized by high unemployment and low consumer confidence, mortgage rates could dip to approximately 4.0% to 5.0%. This scenario would see the Federal Reserve lowering interest rates to stimulate the economy and support borrowers.
3. Stagnant Economy Scenario
Should the economy experience stagnation, where growth is minimal, mortgage rates may hover around 5.0% to 6.0%. In this scenario, economic uncertainty would lead to cautious lending practices but prevent significant rate increases due to lower demand.These hypothetical environments illustrate how varying economic conditions can affect mortgage rates, providing homeowners and potential buyers with a framework for decision-making. By understanding these scenarios, individuals can better navigate the complexities of mortgage financing in an ever-changing market.
Closing Notes
In summary, understanding mortgage rates is more than just knowing the numbers; it’s about grasping the underlying factors that influence those numbers and how they can impact financial decisions. By keeping an eye on economic trends and employing smart strategies, borrowers can enhance their chances of obtaining the best mortgage rates, ultimately paving the way for successful real estate investments.
As the housing market evolves, staying informed will be key to making sound financial choices.
User Queries
What factors should I consider when choosing a mortgage rate?
Consider your financial situation, the length of time you plan to stay in the home, and whether you prefer the stability of fixed rates or the potential for lower initial costs with adjustable rates.
How often do mortgage rates change?
Mortgage rates can change daily based on market conditions, economic data releases, and changes in the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy.
Can I negotiate my mortgage rate?
Yes, many lenders are open to negotiation. If you have a strong credit score and a solid financial profile, you may be able to secure a better rate.
How do I know if I’m getting a good mortgage rate?
Research current market rates and compare them with the quote you receive. Additionally, consult with a financial advisor to assess your offer.
What is the impact of my credit score on my mortgage rate?
A higher credit score typically leads to lower mortgage rates, while a lower score can result in higher rates, affecting your overall borrowing costs.