The journey of online shopping is seamless, thanks to the unsung heroes of the digital marketplace: payment gateways. These platforms not only facilitate transactions but also ensure that sensitive information remains secure during the process. By acting as intermediaries between customers and merchants, payment gateways play a pivotal role in the e-commerce ecosystem, enabling businesses to thrive in a competitive landscape.
From encryption techniques to various types of gateways, understanding the intricate workings of payment gateways can empower businesses to make informed decisions. By grasping these concepts, companies can enhance their payment processes, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Understanding the Fundamental Concepts of a Payment Gateway
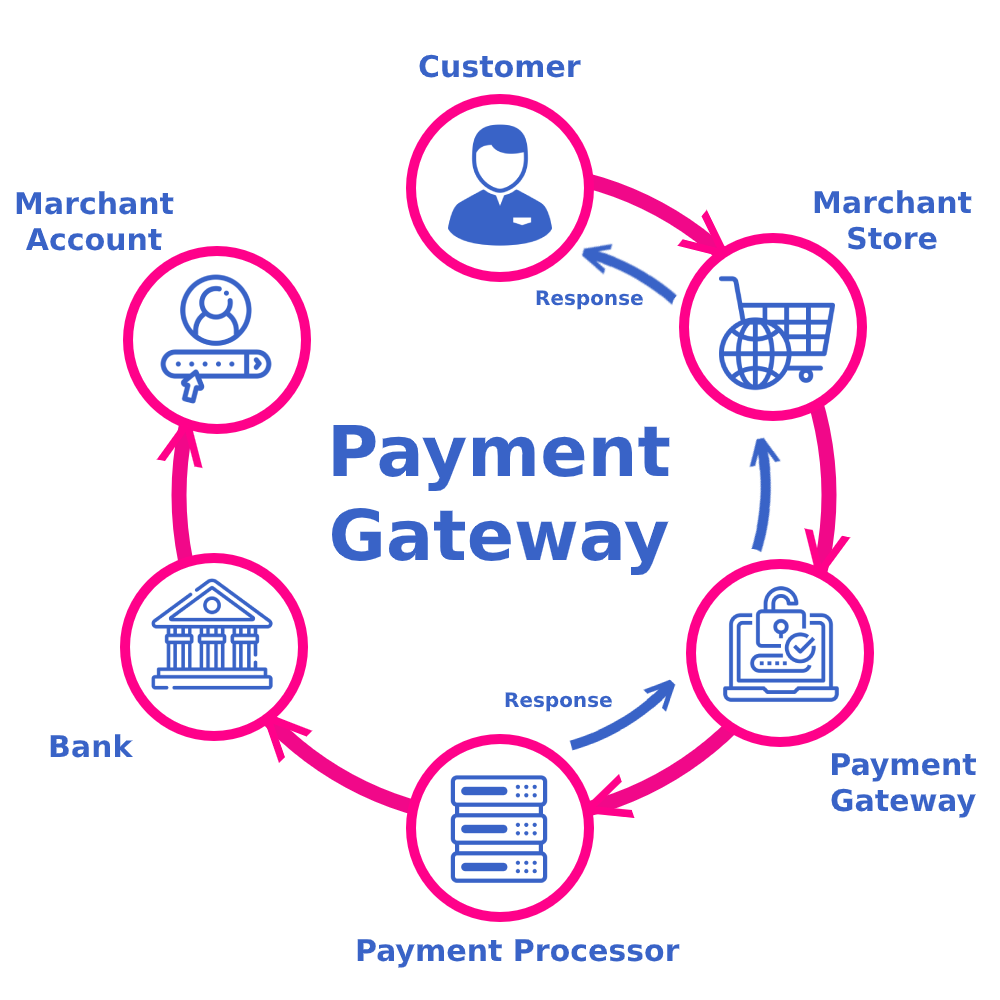
A payment gateway is a crucial component of online transactions, acting as a bridge between a customer’s payment method and the merchant’s bank. Its primary purpose is to process credit card payments and other electronic transactions securely. By encrypting sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, and facilitating the transfer of data between the customer, the merchant, and the bank, a payment gateway ensures that transactions are conducted smoothly and safely.
This process involves several steps, including authorization, funding, and reporting, all of which are pivotal in ensuring that the merchant receives their funds and the customer’s information remains protected.The main components of a payment gateway consist of the following elements, each playing a specific role in the transaction process:
Main Components of a Payment Gateway
The functionality of a payment gateway relies on several key components that work together to facilitate transactions. Understanding these components helps in grasping how online payments are processed:
- Merchant Account: This is a type of bank account that allows businesses to accept payments via credit and debit cards. It serves as a temporary holding place for funds before they are transferred to the business’s main bank account.
- Payment Processing Engine: This engine handles the actual transaction processing, including authorization and settlement. It communicates with the bank to verify the customer’s payment information.
- API (Application Programming Interface): APIs are used to connect the payment gateway with a website or application, enabling the exchange of transaction data and ensuring that the gateway can communicate with various banks and financial institutions.
- Security Protocols: Most payment gateways implement protocols like SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) to protect data transmitted between the customer and the merchant.
Security is a paramount concern in the payment gateway process, as it involves handling sensitive financial information. Encryption plays a significant role in safeguarding this data. When a customer enters their payment details, the payment gateway encrypts this information to prevent unauthorized access during transmission. The encrypted data is then sent to the payment processor, which decrypts it for verification.
“The use of encryption ensures that sensitive data remains confidential and secure throughout the transaction process.”
In addition to encryption, payment gateways also employ fraud detection mechanisms and adhere to standards such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) to enhance security measures. This helps in preventing fraudulent transactions and protecting both merchants and customers from potential threats. As online shopping continues to grow, the importance of secure payment gateways becomes increasingly evident, making them essential for any business engaged in e-commerce.
The Different Types of Payment Gateways Available in the Market
Payment gateways serve as crucial intermediaries between customers and merchants, facilitating seamless online transactions. Understanding the different types of payment gateways available is essential for businesses to choose the right solution that aligns with their operational needs and customer preferences. This overview categorizes payment gateways into hosted, self-hosted, and API-based solutions, providing insights into their unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
Hosted Payment Gateways
Hosted payment gateways redirect customers to an external server to complete their transactions. This ensures that sensitive payment information is handled securely, reducing the burden of compliance on merchants. Popular providers in this category include PayPal, Stripe, and Authorize.Net.
- Advantages:
-
Enhanced security is provided as sensitive data is processed by the gateway, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
- Ease of integration for small businesses, with minimal technical setup required.
- Automatic updates and maintenance handled by the payment provider.
-
- Disadvantages:
- Redirecting customers can lead to a less seamless user experience.
- Fees may be higher due to the service provided by the gateway.
- Limited customization options for the payment process.
Self-Hosted Payment Gateways
Self-hosted payment gateways allow businesses to process transactions on their own server, offering greater control over the payment experience. Examples include WooCommerce Payments and Magento’s in-built payment functionalities.
- Advantages:
-
Complete control over the payment experience, allowing for extensive customization.
- Potentially lower transaction fees as there are fewer intermediaries involved.
- Ability to maintain a consistent brand experience throughout the payment process.
-
- Disadvantages:
- Increased responsibility for security and compliance, necessitating additional resources.
- More complex setup and ongoing maintenance compared to hosted solutions.
- Higher initial development costs can deter smaller businesses.
API-Based Payment Gateways
API-based payment gateways provide developers with the tools to integrate payment processing directly into their applications. This allows for a highly customizable and seamless transaction experience. Notable providers include Braintree, Square, and Adyen.
- Advantages:
-
Full customization allows businesses to create a unique user experience tailored to their needs.
- Ability to add advanced features like subscription billing and fraud detection.
- Direct integration into existing systems enhances operational efficiency.
-
- Disadvantages:
- Requires in-depth technical knowledge for implementation and maintenance.
- Potentially higher development costs due to the need for skilled developers.
- Challenges in ensuring security and compliance, requiring constant updates and monitoring.
Key Features to Look for When Choosing a Payment Gateway
Selecting the right payment gateway is crucial for any business that engages in online transactions. A reliable payment gateway not only facilitates smooth transactions but also enhances customer trust and satisfaction. Understanding the key features to look for can significantly impact your business’s efficiency and security.When evaluating payment gateways, it’s essential to focus on several core features that can determine the effectiveness of the service.
These features include multi-currency support, fraud detection, transaction fees, user experience, and integration capabilities. Each of these points plays a vital role in ensuring that your payment processing needs are met efficiently and securely.
Essential Features of Payment Gateways
The following key features are critical when evaluating various payment gateway options. These aspects not only serve the immediate transaction needs but also contribute to long-term business growth and security.
- Multi-Currency Support: Allows businesses to accept payments in various currencies, catering to a global audience.
- Fraud Detection: Incorporates advanced algorithms to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions, thus safeguarding both the business and its customers.
- Transaction Fees: Varies among providers; understanding fee structures helps businesses choose gateways that align with their financial goals.
- User Experience: A simplified checkout process enhances customer satisfaction and reduces cart abandonment rates.
- Integration Capabilities: Ability to integrate seamlessly with existing platforms, such as eCommerce sites and accounting software, streamlining operations.
Comparison of Features Among Leading Payment Gateways
An effective way to evaluate the different payment gateways available is through a direct comparison of their features. Below is a table highlighting the essential features of some leading payment gateways:
| Payment Gateway | Multi-Currency Support | Fraud Detection | Transaction Fees | User Experience | Integration Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PayPal | Yes | Advanced | Variable | High | Wide range of integrations |
| Stripe | Yes | Comprehensive | Low | Very High | Extensive API support |
| Square | Limited | Moderate | Fixed | High | Easy integration with Square products |
| Braintree | Yes | Robust | Variable | High | Excellent API support |
Benefits of Specific Features for Different Types of Businesses
Understanding how specific features can benefit various business types is essential for making an informed choice. For example, eCommerce retailers especially benefit from multi-currency support as it allows them to cater to international customers effectively. In contrast, subscription-based services may prioritize fraud detection features to minimize risks associated with recurring payments.Businesses that have a large volume of transactions, such as marketplaces, can take advantage of payment gateways with lower transaction fees, ensuring that more of their revenue is retained.
Meanwhile, small businesses or startups might prefer user-friendly gateways that offer straightforward integration and a seamless checkout experience to facilitate growth without overwhelming complexity.
Choosing the right payment gateway can significantly influence customer trust and overall sales performance.
The Process of Integrating a Payment Gateway into an E-commerce Website
Integrating a payment gateway into your e-commerce website is a crucial step in enabling online transactions. This process allows businesses to securely process customer payments, ensuring a smooth shopping experience. Understanding the steps involved in this integration is essential for developers and store owners alike. The integration of a payment gateway involves several methodical steps, each requiring attention to detail for successful implementation.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your online store can handle transactions securely and efficiently while providing a seamless experience for your customers.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Integration
The integration of a payment gateway into an online store typically follows these key steps:
1. Choose a Payment Gateway Provider
Research and select a payment gateway that meets your business needs and budget. Popular providers include Stripe, PayPal, and Authorize.Net.
2. Create an Account
Sign up for an account with your chosen payment gateway provider. This will grant you access to the necessary tools and resources for integration.
3. Obtain API Keys
After setting up your account, you will need to generate API keys. These keys are essential for connecting your website to the payment gateway securely.
4. Install Required Libraries
Depending on your website’s platform (like WooCommerce, Shopify, or Magento), you may need to install specific libraries or plugins provided by the payment gateway to facilitate integration.
5. Configure Payment Gateway Settings
Access the payment gateway settings in your e-commerce platform and enter the API keys, along with other required information such as merchant identification and payment preferences.
6. Implement the Payment Form
Create a payment form on your website where customers can enter their payment information. Ensure that this form is secure and compliant with industry standards.
7. Test Transactions
Perform test transactions using sandbox credentials provided by your payment gateway to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
8. Go Live
Once confident in the integration, switch from the test mode to live mode. Ensure all settings are correctly configured for real transactions.
Testing the Payment Gateway After Integration
Testing is vital after integrating a payment gateway to guarantee that it functions properly under various conditions. Follow these guidelines for thorough testing:
Use Sandbox Mode
Engage with the payment gateway’s sandbox mode to simulate transactions without processing real payments.
Conduct Different Transaction Types
Test multiple transaction types, including successful payments, declined transactions, and refunds, to ensure the system can handle various scenarios.
Verify User Experience
Assess the user interface and checkout process from a customer’s perspective, ensuring it is intuitive and straightforward.
Check Security Protocols
Confirm that the transaction data is encrypted and that the payment process adheres to PCI DSS standards.
Review Notifications
Test the order confirmation and payment notification processes to ensure customers receive timely updates.
Checklist of Common Mistakes to Avoid
To streamline the integration process and enhance functionality, be aware of the following common mistakes:
Inadequate Security Measures
Failing to implement proper encryption and security protocols can expose sensitive customer data.
Ignoring Testing
Skipping or rushing through testing can result in significant errors during live transactions.
Incorrect API Configuration
Misconfiguration of API keys or settings can prevent transactions from processing correctly.
Lack of Customer Support Information
Not providing customers with clear support options can lead to frustration during payment issues.
Failing to Update Payment Plugins
Outdated payment gateway plugins or libraries can lead to compatibility issues and security vulnerabilities.By adhering to these steps, guidelines, and checklists, you can successfully integrate a payment gateway into your e-commerce website, providing a secure and efficient payment process for your customers.
The Financial Implications of Using a Payment Gateway for Businesses
Using a payment gateway can significantly impact a business’s financial landscape. Understanding the fee structures and how they affect overall profitability is crucial for business owners. This knowledge helps in making informed decisions that can lead to savings and better financial management.Different payment gateways have varying fee structures that can influence the bottom line. Generally, these fees can be classified into transaction fees, monthly fees, setup fees, and chargeback fees.
Each type of fee plays a role in how much a business ultimately spends on payment processing. As a result, businesses must analyze these costs to determine which gateway aligns best with their financial goals.
Fee Structures of Payment Gateways
The fee structure of payment gateways can vary significantly from one provider to another. Below are common types of fees associated with payment gateways:
- Transaction Fees: This fee is charged for each transaction processed through the gateway. It is typically a percentage of the sale plus a fixed amount.
- Monthly Fees: Some payment gateways charge a monthly service fee, regardless of transaction volume. This fee can be a flat rate or tiered based on usage.
- Setup Fees: Certain providers may charge an initial setup fee when onboarding a new merchant. This fee can vary depending on the complexity of the integration.
- Chargeback Fees: If a customer disputes a charge, the merchant may incur a chargeback fee, which can add up quickly if not managed properly.
Analyzing these fees is essential for businesses, as they can directly affect profitability. For instance, a gateway with lower transaction fees may seem attractive, but higher monthly fees could negate potential savings.
Factors Influencing Transaction Costs
Several factors can influence the transaction costs a business incurs when using a payment gateway. Understanding these can help businesses effectively manage and potentially reduce these fees.
- Type of Business: Different industries face varying levels of risk associated with transactions, impacting the fees charged by payment gateways. For example, e-commerce businesses may face higher fees than brick-and-mortar stores.
- Transaction Volume: Higher transaction volumes may qualify businesses for lower rates due to negotiated pricing structures, highlighting the importance of building a customer base.
- Payment Methods: Different payment methods (credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets) can have varying fees associated with them. Businesses should encourage the use of lower-cost methods when possible.
By understanding and managing these factors, businesses can strategically select the most cost-effective payment gateway solution.
Case Studies of Cost Reduction
Real-life examples illustrate how businesses have successfully reduced their payment processing costs through the strategic selection of payment gateways.One notable case is a small e-commerce retailer that switched from a traditional payment processor to a specialized payment gateway that catered to its industry. By renegotiating transaction fees based on their average sales volume, they reduced their processing costs by 30%.
This switch also included more favorable terms for chargeback handling, lowering their overall cost exposure.Another example involves a subscription-based service that integrated a payment gateway offering a flat-rate fee structure. Initially paying a percentage-based fee, the company switched to a flat-rate model that better suited their steady transaction volume, resulting in an estimated savings of 20% annually.These cases demonstrate that with careful evaluation and strategic changes, businesses can effectively manage and reduce their payment processing costs, enhancing overall profitability.
Exploring the Future of Payment Gateways and Emerging Technologies

The landscape of payment gateways is rapidly evolving, largely due to the integration of innovative technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence. These advancements are not only streamlining payment processes but also enhancing security and user experience. As we delve deeper into these technologies, it becomes clear that the future of payment gateways will be significantly shaped by these emerging trends.
Impact of Blockchain and AI on Payment Gateways
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way transactions are processed by offering a decentralized ledger that enhances transparency and security. This technology eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and times. Additionally, artificial intelligence is playing a crucial role in fraud detection and risk assessment. AI algorithms analyze transaction patterns to identify anomalies, providing a robust defense against fraudulent activities.
Key advantages of integrating blockchain and AI include:
- Improved Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic features and AI’s predictive analytics create an environment with reduced fraud risk.
- Faster Transactions: Decentralized processing speeds up transactions by eliminating third-party delays.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower operational costs can be achieved by reducing the involvement of traditional financial institutions.
Influence of Mobile Payments and Digital Wallets
The increasing prevalence of mobile payments and digital wallets is transforming payment gateway trends. Consumers are gravitating towards convenience, preferring to make transactions via their smartphones rather than traditional methods. This shift is pushing payment gateways to adapt to mobile-first strategies.The growing importance of mobile payments includes:
- Accessibility: Mobile wallets enable users to transact anytime, anywhere, providing a level of convenience that traditional cash transactions cannot offer.
- User Experience: Enhanced user interfaces in mobile wallets are making payments quicker and more intuitive.
- Integration with Loyalty Programs: Many digital wallets operate seamlessly with loyalty programs, creating additional value for users.
Challenges and Opportunities for Payment Gateways
As payment gateways embrace these technological advancements, they will encounter both challenges and opportunities in the coming decade. Anticipated challenges and opportunities include:
- Regulatory Compliance: The evolving regulatory landscape surrounding digital currencies and mobile transactions poses a challenge for payment gateways to remain compliant while innovating.
- Cybersecurity Threats: As digital transactions increase, so do the sophistication of cyber threats, necessitating ongoing investments in security measures.
- Market Competition: The rise of fintech companies entering the payment space may create intense competition, leading to innovation but also market saturation.
- Global Expansion: Payment gateways have the opportunity to expand into emerging markets, leveraging mobile technology to reach underserved populations.
The Role of Payment Gateways in Enhancing Customer Experience
In today’s digital marketplace, payment gateways play a crucial role in shaping the shopping experience for customers. They serve as the bridge between consumers and merchants, enabling secure and efficient transactions while providing a host of features that enhance user satisfaction. By integrating user-friendly interfaces and seamless checkout processes, payment gateways significantly contribute to a positive shopping journey. One of the primary benefits of payment gateways is their ability to streamline the checkout process, which is often a make-or-break moment for customers.
A well-designed payment interface can reduce cart abandonment rates and improve overall sales. Payment gateways simplify the payment experience by offering a variety of payment options, including credit cards, digital wallets, and bank transfers, tailored to meet the diverse preferences of consumers.
User-Friendly Interfaces and Seamless Checkout Processes
The significance of user-friendly interfaces cannot be overstated when it comes to payment gateways. A clear and intuitive design helps customers navigate the payment process without confusion or frustration. The following factors contribute to a seamless checkout experience:
- Minimal Steps: Simplifying the checkout process to require as few steps as possible encourages users to complete their purchases.
- Mobile Optimization: As more consumers shop via mobile devices, gateways that are optimized for mobile can enhance user satisfaction and accessibility.
- Multiple Payment Options: Offering various payment methods caters to different customer preferences, making transactions more convenient.
- Real-Time Feedback: Providing instant confirmation and feedback during the payment process builds trust and reassures customers that their transaction is secure.
Effective customer support services offered by payment gateways also play a critical role in enhancing user satisfaction. A responsive and knowledgeable support team can address customer inquiries or issues promptly, leading to a more positive experience.
Impact of Customer Support Services on User Satisfaction
The quality of customer support can significantly affect a customer’s perception of the entire shopping experience. Payment gateways that prioritize customer assistance can create a sense of reliability and trust. Key aspects of effective customer support include:
- 24/7 Availability: Offering round-the-clock support ensures that customers can receive assistance whenever they need it, regardless of time zones.
- Multiple Communication Channels: Providing various ways to contact support, such as live chat, email, and phone, accommodates customer preferences.
- Comprehensive FAQs: A well-organized FAQ section can empower customers to find solutions quickly without needing to contact support.
- Proactive Communication: Keeping customers informed about any issues, updates, or changes related to their transactions fosters transparency and trust.
In essence, payment gateways are instrumental in creating an enjoyable shopping experience. Their user-friendly interfaces, seamless checkout processes, and effective customer support services are essential components that contribute to overall customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Addressing Common Security Concerns Associated with Payment Gateways
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, security remains a top priority for businesses utilizing payment gateways. As transactions increasingly shift online, understanding and addressing security concerns is crucial for both businesses and customers. Payment gateways face various threats that can compromise sensitive information, and it is imperative to implement robust measures to ensure security.Payment gateways encounter several prevalent security threats, including data breaches, phishing attacks, and payment fraud.
These threats can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. To combat these risks, payment gateways implement multiple layers of security measures designed to protect sensitive customer data. These include encryption protocols, tokenization, and compliance with industry standards such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard).
Prevalent Security Threats to Payment Gateways
Understanding the specific security threats that payment gateways face is essential for developing effective defense strategies. The following are some of the most common threats encountered:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive customer data, often due to vulnerabilities in the system.
- Phishing Attacks: Attempts to deceive users into providing personal information through fake websites or emails.
- Payment Fraud: Unauthorized transactions made using stolen credit card information or fake identities.
- Malware and Ransomware: Malicious software that can disrupt services or steal sensitive information.
Security Measures Implemented by Payment Gateways
To effectively safeguard customer data, payment gateways employ a variety of security measures. These measures are designed to detect and prevent potential threats, ensuring a secure transaction environment.
- Encryption: Sensitive data is encrypted during transmission to prevent unauthorized access. This makes it virtually impossible for hackers to decipher the information without the appropriate keys.
- Tokenization: This process replaces sensitive data with unique identifiers or tokens, minimizing the risk of data exposure during transactions.
- Multi-factor Authentication: Additional verification steps are required during the transaction process, ensuring that only authorized users can complete transactions.
- Regular Security Audits: Payment gateways conduct periodic assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security standards.
Best Practices for Businesses Enhancing Payment Gateway Security
In addition to the measures implemented by payment gateways, businesses can adopt best practices to further enhance security. Implementing these practices can help mitigate risks and protect customer information.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly updating payment processing software reduces vulnerabilities and ensures that security patches are applied promptly.
- Educate Employees: Providing training on recognizing phishing attacks and security best practices can significantly reduce human error-related breaches.
- Monitor Transactions: Keeping a close eye on transactions can help identify suspicious activity and prevent fraud in real-time.
- Implement Strong Password Policies: Requiring complex passwords and changing them regularly can help safeguard accounts from unauthorized access.
“Maintaining security in payment processing is a shared responsibility; while gateways provide tools and protocols, businesses must actively participate in safeguarding their transactions.”
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the significance of payment gateways in the realm of e-commerce cannot be overstated. They not only streamline transactions but also enhance security and user experience. As businesses continue to adapt to technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors, investing in the right payment gateway becomes crucial for sustained success and growth.
Questions Often Asked
What is a payment gateway?
A payment gateway is a technology that processes credit card payments for e-commerce websites, ensuring secure transactions between customers and merchants.
Are payment gateways safe?
Yes, payment gateways use encryption and security protocols to protect sensitive customer information during transactions.
What are hosted and self-hosted payment gateways?
Hosted payment gateways redirect customers to a secure page for payment processing, while self-hosted gateways allow payments to be processed directly on the merchant’s website.
How much do payment gateways charge?
Payment gateways typically charge transaction fees, which can vary based on the provider, but may include flat fees, percentage-based fees, or monthly charges.
Can I integrate a payment gateway into my existing website?
Yes, most payment gateways offer APIs and plugins that allow for easy integration into existing e-commerce websites.
What features should I look for in a payment gateway?
Key features include multi-currency support, fraud detection, user-friendly interfaces, and seamless integration options.