Financial forecasting is a crucial aspect of strategic planning that allows businesses to anticipate future financial performance and make informed decisions. Understanding the various methods of financial forecasting, from quantitative to qualitative approaches, can significantly enhance a company’s ability to predict its financial landscape accurately. Companies utilize statistical techniques in financial modeling to tailor their forecasts to specific needs, ensuring that they are not only realistic but also actionable.
As organizations increasingly rely on technology, the integration of advanced software tools and predictive analytics has transformed financial forecasting into a more precise science. The role of historical data and stakeholder involvement cannot be overlooked, as they play vital roles in creating reliable forecasts that consider both internal capabilities and external market influences. When done right, financial forecasting serves as one of the cornerstones of effective financial management.
Financial forecasting methods used in the corporate world are essential to understand for accurate predictions.
Financial forecasting is a critical activity for companies looking to accurately predict their future financial performance. The methods employed can significantly impact decision-making processes, helping businesses navigate uncertainties and capitalize on opportunities. Understanding the various approaches to financial forecasting is essential for executives and analysts alike to ensure that the predictions align with the company’s specific objectives.Among the different financial forecasting methods, two primary categories stand out: quantitative and qualitative approaches.
Each method has its unique strengths and applications, making it important for companies to choose the right one based on their specific needs and the context in which they operate.
Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches
Quantitative forecasting relies on numerical data and mathematical models to predict future outcomes. It is often favored for its objectivity and reliance on historical data. Common statistical techniques used in quantitative forecasting include:
- Time Series Analysis: This method involves analyzing historical data points collected or recorded at specific time intervals. For example, a retail company might analyze past sales data to forecast future revenue trends.
- Regression Analysis: Companies use regression analysis to identify relationships between variables. For instance, a business may assess how changes in marketing expenditure influence sales volume, enabling them to predict future sales based on budget adjustments.
- Moving Averages: This statistical technique smooths out data fluctuations by calculating averages over specific periods, helping businesses to discern underlying trends more clearly. A manufacturing company might use moving averages to forecast future production needs based on seasonal sales patterns.
On the other hand, qualitative forecasting is more subjective, relying on expert judgment and insights rather than numerical data. This approach is particularly useful in situations where historical data is limited or when predicting outcomes for new products or markets. Techniques commonly used in qualitative forecasting include:
- Expert Opinions: Gathering insights from industry experts can provide valuable context for forecasts, especially in emerging markets where data may be sparse.
- Market Research: Conducting surveys or focus groups allows companies to gather consumer opinions and preferences, which can help predict demand for new products.
The significance of selecting the right forecasting method cannot be understated. The choice should align with the organization’s goals, the availability of data, and the market dynamics at play. For example, a technology startup launching a new product may lean towards qualitative methods for initial forecasts, relying on expert opinions and market research to gauge potential demand. Conversely, a well-established company with extensive historical sales data might prefer quantitative techniques to provide more reliable projections.Understanding these methods enables companies to make informed strategic decisions.
Utilizing the appropriate forecasting method can lead to better resource allocation, improved budgeting, and ultimately, enhanced financial performance. Failure to select the right method may result in poor predictions, leading to financial losses and missed opportunities. Therefore, understanding both quantitative and qualitative forecasting methods is essential for organizations striving for accuracy in their financial predictions.
The role of technology in enhancing financial forecasting capabilities in businesses requires thorough examination.
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the way businesses approach financial forecasting. The integration of sophisticated software tools and predictive analytics has led to significant improvements in forecasting accuracy, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time data insights. By harnessing the power of technology, companies can navigate the complexities of financial environments with greater precision and agility.
Impact of Software Tools and Predictive Analytics on Accuracy, Financial forecasting
The deployment of software tools and predictive analytics has created a paradigm shift in financial forecasting. These technologies allow businesses to analyze vast amounts of historical data, identify trends, and construct models that predict future financial outcomes. The accuracy of forecasts has improved due to advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques which refine predictions based on past performance. Some widely used technology platforms that assist in financial modeling include:
- Oracle Hyperion: A comprehensive suite that offers budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting solutions, enhancing data consolidation and analysis.
- SAP Analytics Cloud: This platform combines business intelligence with predictive analytics, enabling users to visualize data and forecast financial scenarios effectively.
- IBM Planning Analytics: Powered by IBM’s Watson, this tool uses AI-driven insights to facilitate better planning and forecasting processes, allowing for scenario-based forecasting.
- Microsoft Excel with Add-ins: While Excel is a traditional tool, its capabilities can be enhanced with add-ins like @RISK that incorporate Monte Carlo simulations for more robust forecasts.
Automation is a game-changer in the landscape of financial forecasting. By automating repetitive tasks such as data entry, report generation, and basic analysis, businesses can significantly reduce human error and free up valuable resources. Automation tools can quickly gather and process data from multiple sources, providing real-time insights that inform decisions. For instance, cloud-based solutions can seamlessly integrate with existing data systems, allowing businesses to generate forecasts within minutes rather than days.
This not only accelerates the forecasting process but also enables more frequent updates as new data becomes available. The capacity for scenario analysis has also expanded, empowering financial teams to assess various potential outcomes and strategies simultaneously. Furthermore, automated forecasting systems can learn from past forecasts, continuously improving their predictive capabilities over time. Organizations like Netflix utilize sophisticated algorithms to forecast viewer preferences and trends, demonstrating the practical application of automation in financial forecasting.
In summary, technology, through software tools and automation, is transforming financial forecasting, providing businesses with the accuracy, speed, and flexibility needed to thrive in a dynamic economic landscape.
Real-world implications of inaccurate financial forecasting can lead to severe consequences for organizations.
Inaccurate financial forecasting can have devastating effects on organizations, impacting their operational efficiency, strategic decisions, and overall financial health. By failing to anticipate market trends, consumer demand, and economic fluctuations, businesses risk misallocating resources, incurring unexpected costs, or facing revenue shortfalls. Such errors can lead to a cascade of issues that may threaten the very existence of a company.
Common pitfalls in financial forecasting
Understanding the pitfalls in financial forecasting is vital for organizations to mitigate risks and enhance accuracy. Here are some common challenges that can arise:
- Over-reliance on historical data: While historical data provides a foundation for forecasts, it may not account for changing market dynamics, leading to misguided projections. Organizations that solely depend on past performance may overlook significant shifts in consumer behavior or economic conditions.
- Inadequate market research: Poorly conducted market research can result in forecasts that are disconnected from actual consumer needs. When businesses lack insight into their market landscape, they risk making decisions based on flawed assumptions, ultimately affecting product development and marketing strategies.
- Ignoring external factors: Financial forecasting must consider external variables such as economic trends, regulatory changes, and competitive landscapes. Ignoring these factors could lead to substantial deviations from forecasted outcomes, causing companies to misjudge their financial positioning.
- Failure to involve key stakeholders: Forecasting is often a collaborative effort that requires input from various departments, including sales, marketing, and finance. A lack of cross-departmental communication can result in a fragmented approach, leading to inaccuracies in the overall forecast.
Case studies of companies affected by poor forecasting
Several companies have faced significant challenges due to inadequate forecasting practices. For instance, Ford Motor Company’s decision to produce the Edsel model in the late 1950s stemmed from overly optimistic sales forecasts. The company anticipated high demand, but it misjudged consumer preferences, leading to massive financial losses and an eventual retraction of the vehicle. Similarly, in 2015, Target’s foray into Canada resulted in considerable financial losses.
The company relied on overly aggressive sales estimates and inadequate preparation for the Canadian market, resulting in store closures and a tarnished reputation.
Importance of regular review and adjustment of forecasts
Regularly reviewing and adjusting financial forecasts is crucial for maintaining accuracy and relevance. Market conditions, consumer behavior, and economic indicators are dynamic; thus, forecasts should evolve in tandem. A proactive approach allows organizations to identify discrepancies early, enabling timely adjustments that can minimize negative impacts on business operations.In the fast-paced business environment, established companies like Procter & Gamble continuously refine their forecasting methodologies to align with emerging trends and consumer insights.
This practice not only enhances the reliability of forecasts but also fosters agility in decision-making.Regular adjustments can be facilitated through the implementation of robust forecasting models that incorporate real-time data and analytics. By leveraging advanced technologies, businesses can gain insights into predictive trends, ultimately allowing for more strategic planning.The overall effectiveness of financial forecasting lies in its ability to guide informed decision-making.
Organizations that prioritize regular reviews and adjustments position themselves to navigate uncertainties and seize new opportunities, ensuring long-term sustainability and growth.
The relevance of historical data in shaping future financial forecasts cannot be overstated.: Financial Forecasting

In the realm of financial forecasting, the significance of historical data cannot be overstated. Historical performance serves as a critical foundation for any financial projections, providing insights into past trends, consumer behavior, and market dynamics. By understanding what has happened before, organizations can make informed predictions about future performance, reducing uncertainty and enhancing decision-making processes.Proficient financial forecasting relies on the analysis of past data to identify patterns and trends.
These historical insights become essential in recognizing cyclical behaviors, seasonal variations, and long-term growth trajectories. A comprehensive trend analysis allows analysts to project future outcomes based on observed historical performance, effectively minimizing the risks associated with forecasting errors. For instance, if a company sees a consistent increase in quarterly sales during the holiday season over several years, it can reasonably anticipate similar patterns in the future, adjusting inventory and marketing strategies accordingly.
Methods for collecting and analyzing historical data relevant to financial forecasting
The process of collecting and analyzing historical data is vital to enhancing accuracy in financial forecasting. There are several effective methods to gather this data, which can include:
- Internal Data Sources: Organizations often maintain their own financial records, including sales data, expense reports, and customer transaction histories. Utilizing this internal data allows for a tailored analysis that reflects the company’s unique circumstances.
- Industry Reports: Third-party industry reports and market analysis provide a broader context, reflecting sectoral trends and economic indicators. These reports often synthesize data from multiple businesses, offering insights into market potential and competitive dynamics.
- Publicly Available Financial Statements: For publicly traded companies, financial statements are accessible and provide invaluable data for comparative analysis. Analyzing these reports can help forecast performance based on industry norms.
- Market Research Surveys: Conducting surveys can yield qualitative data regarding consumer preferences and market trends. This qualitative insight can support quantitative data, creating a fuller picture of market dynamics.
Once the data is collected, effective analysis is key to improving forecasting accuracy. Analysts can utilize various techniques, such as:
- Time Series Analysis: This statistical technique uses historical data points to forecast future values, relying on the assumption that past patterns will continue into the future. For example, a business might apply time series analysis to sales data to project future revenue.
- Regression Analysis: By evaluating the relationship between variables, regression analysis helps in understanding how different factors influence financial outcomes. For instance, a company might analyze the correlation between advertising spend and sales growth.
- Moving Averages: This method helps smooth out fluctuations in data, allowing for a clearer view of trends over time. A moving average can help to identify long-term growth trends by filtering out short-term volatility.
By employing these methods and analyses, businesses not only improve the accuracy of their financial forecasts but also position themselves to capitalize on future opportunities, ensuring a robust financial strategy.
Utilizing historical data effectively is a cornerstone of precise financial forecasting, guiding businesses in their strategic planning and decision-making.
Stakeholder involvement in the financial forecasting process is crucial for accuracy and acceptance.
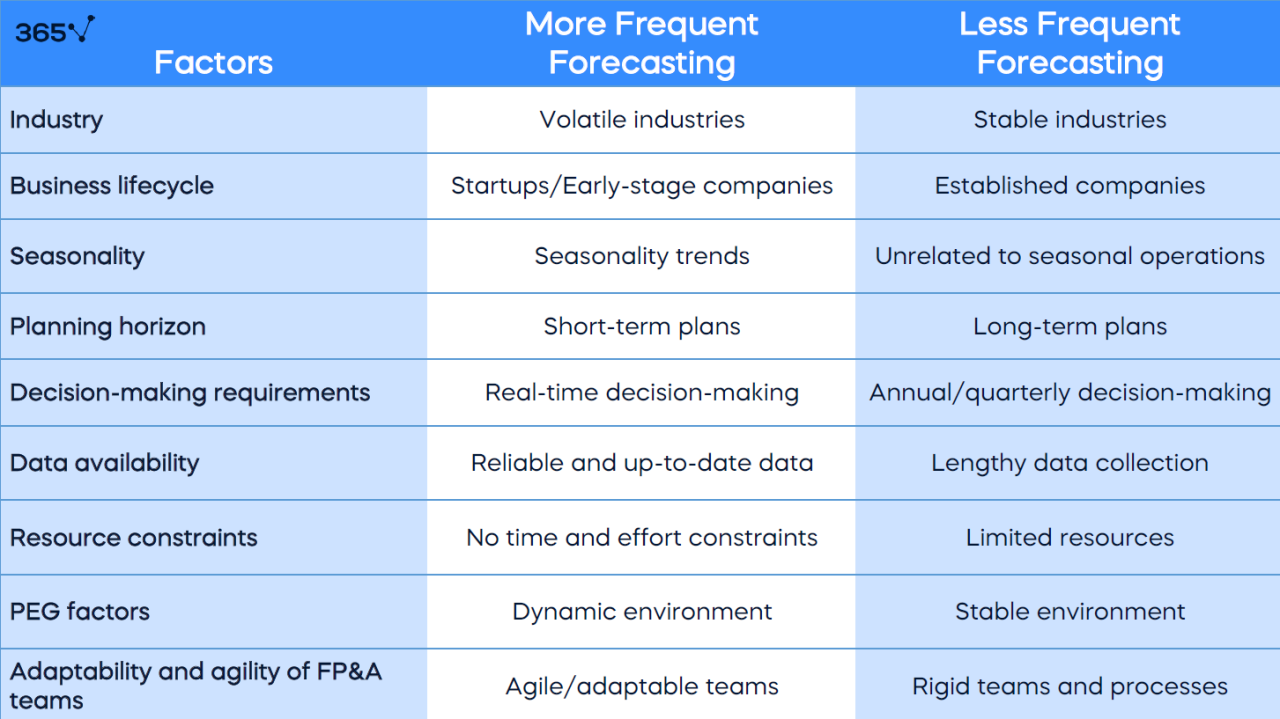
The accuracy of financial forecasting largely hinges on the involvement and collaboration of various stakeholders across the organization. When departments such as finance, operations, and marketing work together, they can create a more comprehensive and reliable forecasting model. The insights gathered from diverse perspectives not only enhance the accuracy of forecasts but also foster a sense of ownership among stakeholders, increasing the likelihood of acceptance and implementation of the forecasted plans.Collaboration among different departments is essential for enriching the forecasting process.
Each department carries unique insights that contribute to a more nuanced understanding of business dynamics. For instance, finance provides historical data and budgeting constraints, while operations can offer information about supply chain capabilities and potential disruptions. Marketing brings valuable perspectives on market trends, consumer behavior, and promotional strategies that are crucial for estimating future revenue streams. By pooling these insights, organizations can create a more robust and accurate financial forecast.
Enhancing Forecast Reliability Through Stakeholder Feedback
Engaging stakeholders in the forecasting process allows organizations to refine their forecasts based on feedback from those who will use the data. This step is critical, as stakeholder input can highlight potential blind spots or assumptions that may not hold true. For example, if the marketing department predicts a surge in product demand but the operations team identifies capacity limitations, this disparity needs to be addressed to ensure the forecast is realistic.To effectively involve stakeholders in the forecasting process, organizations should consider the following structured steps:
1. Establish Clear Objectives
Begin by defining the goals of the forecasting process. This includes what data is needed and what decision-making it will support. Having clear objectives helps in aligning all stakeholders toward a common purpose.
2. Identify Key Stakeholders
Determine which departments and individuals should be involved based on their expertise and impact on the forecasting process. This typically includes finance, marketing, operations, and sales teams.
3. Set Up Collaborative Meetings
Organize regular meetings that bring these stakeholders together to discuss forecasting assumptions, data, and insights. These meetings encourage open dialogue and collaboration, ensuring that everyone’s views are considered.
4. Gather and Analyze Data
Collect relevant data from all departments involved in the forecasting process. This data should be analyzed collectively to identify patterns, trends, and potential discrepancies.
5. Facilitate Feedback Loops
Create mechanisms for ongoing feedback throughout the forecasting process. This can include surveys, one-on-one discussions, and collaborative workshops, providing stakeholders with opportunities to voice their insights and concerns.
6. Adjust Forecasts Based on Input
After gathering feedback, refine the forecasts accordingly. Implement changes that reflect the collective insights of all departments, ensuring the forecast is both realistic and actionable.
7. Document Assumptions and Rationale
Clearly document the assumptions made during the forecasting process and the rationale behind them. This transparency helps stakeholders understand the basis of the forecasts and builds trust in the process.
8. Review and Revise Regularly
Financial forecasting is not a one-time event. Establish regular review cycles to update forecasts based on new data and changes in market conditions, ensuring that stakeholders remain engaged with the evolving process.By systematically involving stakeholders in these ways, organizations can significantly enhance the accuracy and acceptance of their financial forecasts, leading to improved decision-making and strategic planning.
External factors influencing financial forecasts should be recognized and analyzed for a comprehensive approach.
In the realm of financial forecasting, the landscape is seldom static. Factors outside a company’s direct control can profoundly affect predictions and outcomes. Economic indicators, market trends, and regulatory changes serve as pivotal components that need to be integrated into any reliable forecasting model. Understanding these external influences allows businesses to adapt and navigate uncertainties effectively.Recognizing the role of external factors is crucial, as they can significantly alter financial projections.
Economic indicators such as GDP growth rates, unemployment figures, inflation rates, and consumer confidence levels provide a backdrop against which financial forecasts are made. For instance, a sudden spike in inflation may lead to increased costs for raw materials, subsequently impacting production budgets and profit margins. Market trends, including shifts in consumer behavior and technological advancements, also play a significant role.
Companies that fail to account for a growing trend towards sustainability may find themselves outpaced by competitors who are adapting their products and services to meet evolving customer preferences.
Impact of Geopolitical Events on Financial Predictions
Geopolitical events can swiftly change the financial landscape, making it essential for organizations to factor these occurrences into their forecasting models. Examples of such events include trade wars, political unrest, and natural disasters. For instance, the trade tensions between the United States and China have led to increased tariffs, disrupting supply chains and affecting businesses globally. These changes can result in revised revenue projections and impact stock prices.Additionally, events like the COVID-19 pandemic have illustrated how unforeseen circumstances can derail economic stability.
Many companies had to rapidly adjust their forecasts as lockdown measures affected consumer spending and operational capabilities. The effect of such events can linger long after the immediate crisis has passed, necessitating ongoing adjustments in forecasting processes to align with new market realities.The importance of integrating external analysis into forecasting models cannot be overstated. By considering a broad spectrum of external influences, businesses can develop more resilient forecasts that stand up to external shocks.
This comprehensive approach not only enhances accuracy but also builds a company’s ability to pivot in response to changes. For example, financial institutions that incorporate economic forecasts into their asset management strategies can better predict fluctuations in interest rates, thereby optimizing their investment portfolios.In summary, acknowledging and analyzing external factors provides a more holistic view of potential financial outcomes, empowering organizations to make informed decisions.
A dynamic approach to forecasting, inclusive of these external variables, is essential for navigating the complexities of today’s business environment.
Ethical considerations in financial forecasting practices must be addressed for credibility and transparency.
In today’s complex financial landscape, ethical considerations in financial forecasting are paramount. The credibility and reliability of forecasts depend heavily on adherence to ethical standards. With increasing scrutiny from stakeholders, companies cannot afford to overlook the implications of their forecasting methods. Ethical forecasting not only enhances reputation but also builds trust, which is essential for sustainable business relationships.The importance of ethical standards in financial forecasting cannot be overstated.
Ethical dilemmas can arise in various forms, such as conflicts of interest, selective data reporting, or misrepresentation of forecasts. For instance, a financial analyst may feel pressured to present overly optimistic projections to satisfy management or investors, potentially leading to significant repercussions if the forecasts prove inaccurate. Additionally, the lack of transparency in the methodologies used can leave stakeholders questioning the validity of the forecasts provided.
Thus, it is crucial for organizations to establish robust ethical guidelines that govern their forecasting practices.
Guidelines for ensuring transparency and accountability in forecasting processes
To maintain credibility and transparency in financial forecasting, organizations should adopt specific guidelines. These guidelines help ensure that forecasting processes are conducted ethically and responsibly.
1. Clear Communication of Assumptions
Clearly Artikel the assumptions underlying forecasts to provide a solid basis for predictions. This includes market conditions, economic indicators, and any other relevant factors that influence estimations.
2. Regular Audits and Reviews
Implement regular audits of forecasting processes to confirm adherence to ethical standards and to identify potential biases or inaccuracies in the data used.
3. Stakeholder Engagement
Involve stakeholders in the forecasting process to foster a culture of transparency. Open discussions can lead to more reliable data and insights.
4. Data Integrity and Accuracy
Ensure that all data used in forecasts is accurate and comes from reputable sources. Misleading data can distort forecasts, leading to poor decision-making.
5. Ethical Training
Provide ongoing training on ethical standards and practices for all personnel involved in financial forecasting to cultivate a culture of integrity.The implications of these ethical practices directly influence stakeholder trust in financial forecasts. When organizations prioritize ethics, they demonstrate a commitment to transparency and accountability, which fosters trust among investors, clients, and employees. Trust is vital because it encourages stakeholders to engage with the organization, invest in its future, and support its initiatives.
For example, Wells Fargo faced significant backlash after unethical practices were uncovered, leading to a loss of customer trust and a decline in stock value. Conversely, companies that maintain ethical forecasting practices, like Procter & Gamble, often enjoy higher investor confidence and customer loyalty, leading to better financial performance. Consequently, ethical forecasting is not merely a regulatory obligation; it is a strategic imperative that can significantly impact an organization’s success and reputation in the marketplace.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, financial forecasting is essential for organizations aiming for sustainable growth and stability. The discussion highlighted the significance of selecting appropriate forecasting methods, embracing technological advancements, and recognizing the impact of historical data and external factors. By integrating ethical considerations and fostering stakeholder collaboration, businesses can enhance the accuracy and credibility of their financial forecasts, ultimately leading to better decision-making and long-term success.
FAQ
What is financial forecasting?
Financial forecasting is the process of estimating future financial outcomes based on historical data, market trends, and economic indicators.
Why is it important to update financial forecasts regularly?
Regular updates to financial forecasts ensure they remain relevant and accurate, reflecting changes in the market environment and internal company dynamics.
How can technology improve financial forecasting?
Technology enhances financial forecasting by providing tools for data analysis, automation, and predictive analytics, leading to increased accuracy and efficiency.
What are common pitfalls in financial forecasting?
Common pitfalls include reliance on inaccurate data, failure to account for external factors, and lack of stakeholder involvement in the forecasting process.
How do economic indicators affect financial forecasting?
Economic indicators provide insights into market conditions, helping businesses adjust their forecasts to account for potential changes in demand and operational costs.