Invesment management plays a pivotal role in shaping the financial future of individuals and institutions alike. By employing strategic approaches to asset allocation and risk management, investment managers guide their clients toward sustainable wealth accumulation. The integration of diverse investment strategies enables investors to navigate market volatility while pursuing their financial goals.
From traditional stock market investments to emerging technologies, the landscape of investment management is constantly evolving. Understanding how these strategies work is essential for anyone looking to enhance their financial security and stability, making this exploration both timely and relevant.
The Importance of Investment Management in Wealth Growth
Investment management plays a crucial role in the accumulation of wealth, acting as a strategic approach that helps individuals and organizations grow their financial resources over time. By efficiently allocating capital, investment management enables investors to optimize their returns while managing risk. It is not merely about picking stocks or bonds; rather, it’s about understanding the market dynamics, aligning investment objectives with personal financial goals, and adapting strategies as circumstances evolve.
With disciplined investment management, one can build a secure and prosperous financial future, making informed decisions that prioritize long-term gains over short-term fluctuations.Effective investment strategies are instrumental in enhancing financial security and stability. They provide a structured framework that enables investors to navigate the often volatile nature of financial markets. A well-managed investment portfolio can weather economic downturns, reduce exposure to risk, and ensure that the individual’s or institution’s financial needs are met over time.
For instance, diversifying investments across various asset classes—such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and mutual funds—can mitigate risks and smooth out returns. This strategic approach not only safeguards wealth but also positions investors to capitalize on growth opportunities as they arise.
Successful Investment Management Strategies
Implementing successful investment management strategies can significantly contribute to wealth accumulation. These strategies often involve a combination of asset allocation, market analysis, and disciplined decision-making. Here are some notable strategies that have proven effective:
- Index Fund Investing: This strategy involves investing in index funds or ETFs that track market indices. It offers broad market exposure and typically lower fees, making it an effective way to achieve steady, long-term growth. For example, investors who adopted this strategy early and remained invested through market cycles have seen substantial returns over decades.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: This approach entails investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, irrespective of market conditions. By doing so, investors can reduce the impact of volatility and avoid the pitfalls of trying to time the market. This method has been a favorite for many long-term investors, as it allows for the accumulation of shares over time at varying prices.
- Value Investing: Popularized by renowned investors like Warren Buffett, value investing focuses on purchasing undervalued stocks that have strong fundamentals. These investments are held long-term until the market recognizes their true value. Many successful investors have built substantial wealth using this strategy, demonstrating the power of patience and thorough research.
- Real Estate Investment: Investing in real estate can provide both capital appreciation and income through rental yields. By strategically acquiring properties in high-demand areas, investors can experience significant wealth accumulation over time, especially when leveraging financing effectively.
“The stock market is filled with individuals who know the price of everything, but the value of nothing.”
Philip Fisher
Different Types of Investment Management Approaches
Investment management is a critical aspect of financial planning, providing investors with various strategies to grow their wealth. Understanding the different approaches can help investors align their goals with the right management style. Among the most prominent strategies are active and passive management, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks.Active management involves a hands-on approach where fund managers actively make investment decisions with the aim of outperforming the market.
This strategy typically includes frequent trading and a focus on market timing, often utilizing research, analysis, and forecasting to identify investment opportunities. Conversely, passive management seeks to replicate the performance of a specific index or benchmark rather than trying to beat it. This is achieved through minimal trading, often involving index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Comparison of Active and Passive Management
The choice between active and passive management depends on an investor’s goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both approaches is essential for making informed decisions.Active Management:
Strengths
Potential for higher returns by capitalizing on market inefficiencies.
Ability to adjust portfolios quickly in response to market changes or economic trends.
Personalized investment strategy tailored to the investor’s risk profile and objectives. –
Weaknesses
Generally higher management fees due to frequent trading and active oversight.
Greater risk of underperformance compared to the market benchmark.
Requires significant research and expertise, which may not be accessible to all investors.
Passive Management:
Strengths
Lower management fees as trading is minimized and strategies are less resource-intensive.
Consistent performance in line with market indices, reducing the risk of underperformance.
Simplicity and ease of understanding for investors unfamiliar with complex market strategies. –
Weaknesses
Limited potential for high returns as it simply follows the market.
Lack of flexibility to respond to market changes or capitalize on opportunities.
Vulnerability to market downturns, as losses can be mirrored in the index being tracked.
The following table summarizes the key factors affecting both investment management approaches:
| Factor | Active Management | Passive Management |
|---|---|---|
| Risk | Higher due to market timing and individual stock selection | Lower as it tracks an index |
| Return | Potential for higher returns, but also higher potential for loss | Typically provides average market returns |
| Management Fees | Higher fees due to active trading and research costs | Lower fees, generally associated with index funds |
| Investor Suitability | Best for those seeking to outperform the market and willing to take on more risk | Ideal for long-term investors looking for consistent returns with reduced costs |
Investment management approaches are not one-size-fits-all; understanding the nuances between active and passive strategies allows investors to align their decisions with their financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment philosophy.
The Role of Technology in Modern Investment Management

Technology has revolutionized the landscape of investment management, driving efficiency and enhancing decision-making processes. In today’s fast-paced financial environment, investment firms leverage various technological advancements to optimize their strategies and improve client outcomes. The integration of technology not only streamlines operations but also facilitates a data-driven approach, enabling managers to analyze vast amounts of information in real time.
Impact of Robo-Advisors and Algorithmic Trading
Robo-advisors and algorithmic trading represent two significant advancements in technology that have transformed traditional investment management practices. Robo-advisors, automated platforms offering financial advice with minimal human intervention, cater primarily to retail investors. These platforms use algorithms to assess an individual’s financial situation and investment goals, recommending tailored investment strategies. The convenience and accessibility of robo-advisors have democratized investment management, allowing investors with smaller capital to benefit from sophisticated portfolio management techniques.Algorithmic trading, on the other hand, employs complex algorithms to execute trades at optimal prices, often in milliseconds.
This technique allows institutional investors to capitalize on market inefficiencies and respond to market changes much faster than human traders. The increased speed and efficiency of algorithmic trading have reshaped market dynamics, introducing new challenges and regulations to ensure fair trading practices.The combination of these technologies has not only increased the accessibility of investment management services but also heightened competition among traditional firms.
Established financial institutions are now integrating robo-advisory services to retain clients and meet changing demands.
Technological Tools for Portfolio Management and Risk Assessment
Investment management has vastly benefited from an array of technological tools designed to enhance portfolio management and risk assessment. These tools help investment managers analyze performance metrics, predict future trends, and manage risk effectively. Some examples of these tools include:
- Portfolio Management Systems: These comprehensive software solutions allow managers to track and analyze portfolio performance, monitor compliance, and optimize asset allocation. Solutions like BlackRock’s Aladdin or Bloomberg Terminal provide analytics that inform investment decisions.
- Risk Management Software: Tools such as RiskMetrics or Barra offer advanced risk analytics, helping firms assess and mitigate potential risks effectively. They allow for scenario analysis and stress testing, ensuring that managers are prepared for market volatility.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Technologies like Microsoft Power BI and Tableau enable investment firms to visualize data trends and insights intuitively. These platforms facilitate deeper analysis and help identify investment opportunities that may not be immediately apparent.
The integration of these tools enables investment managers to make informed decisions, enhance portfolio performance, and effectively manage risk in an increasingly complex market.
Understanding Risk Management in Investment Portfolios
Effective risk management is a cornerstone of successful investment management. It involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks followed by coordinated efforts to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events. As investors navigate through fluctuating markets, understanding how to mitigate risk can lead to more stable returns and safeguard capital.Risk management strategies in investment management are essential for protecting portfolios from unexpected market volatility and downturns.
One of the primary strategies involves the use of derivatives such as options and futures, which can provide a hedge against potential losses in the underlying assets. Additionally, employing stop-loss orders helps investors limit losses on their investments by automatically selling a security when it reaches a certain price. This proactive approach can be particularly beneficial during sudden market sell-offs.Another critical strategy is the assessment and management of leverage.
While borrowing can amplify returns, it also increases the risk of substantial losses. Thus, maintaining a careful balance between using leverage and ensuring that it does not exceed the investor’s risk tolerance is vital. Furthermore, regular stress testing of investment portfolios against various market scenarios allows investors to evaluate how their portfolios may react under different conditions and adjust positions accordingly.
Importance of Diversification and Asset Allocation
Diversification and asset allocation serve as fundamental tools in risk management, aimed at spreading risk across various assets to minimize the impact of any single investment’s poor performance. Diversification involves investing in a variety of securities across different sectors, geographic regions, and asset classes. By doing so, investors can reduce the potential volatility of their portfolios and enhance returns over time.Asset allocation complements diversification by determining the distribution of capital among different asset classes, such as equities, fixed income, real estate, and cash.
A well-crafted asset allocation strategy aligns with an investor’s risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals. For example, a younger investor may favor a higher allocation in equities for growth potential, while a conservative investor may prefer more bonds to ensure stability and income.When assessing and managing risk in investment portfolios, several best practices can be implemented:
Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Periodically evaluate the risk profile of your portfolio to ensure it aligns with your investment objectives. This includes analyzing market conditions, performance metrics, and potential vulnerabilities.
Set Clear Investment Goals
Establishing specific financial goals helps in creating a tailored risk management strategy that defines acceptable risk levels and return expectations.
Utilize Technology and Tools
Leverage analytical tools and software to monitor portfolio performance continuously, identify risks, and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Adopt a Long-Term Perspective
Focus on long-term investment strategies that can weather market volatility, rather than reacting to short-term fluctuations.
Rebalance Regularly
Adjust your asset allocation periodically to reflect changes in market conditions and personal circumstances, ensuring that your portfolio remains aligned with your risk tolerance.Maintaining a disciplined approach to risk management fosters resilience in investment portfolios, ultimately leading to more sustainable financial growth.
Ethical Considerations in Investment Management
Ethical investing has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by a growing awareness of the impact that investments can have on society and the environment. As investors become more conscious of the implications of their financial decisions, it has become essential for investment management to incorporate ethical considerations into their strategies. This approach not only aligns with the values of many investors but also addresses the risks associated with unethical practices, ultimately leading to greater long-term stability and growth.The importance of ethical investing lies in its capability to influence corporate behavior and promote sustainable practices.
By choosing to invest in companies that prioritize social responsibility, investors can advocate for positive change in areas like environmental sustainability, labor rights, and corporate governance. Ethical investing goes beyond mere financial returns; it encourages a holistic view of value that includes social and environmental impact. Investment managers must navigate these ethical waters carefully, balancing the financial interests of their clients with broader societal goals.
Key Principles of Socially Responsible Investing
Socially responsible investing (SRI) is guided by several key principles that shape investment decisions. These principles not only affect how investment managers evaluate potential investments but also contribute to the overall strategy of portfolio construction. Here are some core tenets of SRI:
- Environmental Stewardship: This principle emphasizes the importance of investing in companies that demonstrate sustainable environmental practices. Investments are often steered away from industries that contribute to pollution or resource depletion.
- Social Equity: Investment decisions consider the impact on communities and social justice. Companies that support fair labor practices, diversity, and community engagement are favored.
- Corporate Governance: Strong governance practices are essential for ethical investment. This includes transparency, accountability, and ethical leadership within companies.
- Long-term Value Creation: SRI focuses on companies that prioritize long-term sustainability and value creation over short-term profits, which often leads to more resilient investments.
The integration of these principles into investment decision-making processes has profound implications. Companies that adhere to ethical standards tend to perform better in the long run, as they are less likely to face regulatory fines, reputational damage, or operational disruptions. Several companies have risen to prominence by prioritizing ethical considerations in their investment strategies. For example, Patagonia, an outdoor clothing brand, is well-known for its commitment to environmental sustainability.
The company donates a percentage of its profits to environmental causes and encourages customers to buy less by promoting repair and reuse of its products. Another example is Tesla, which focuses on renewable energy and aims to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy through electric vehicles and solar products. These companies not only attract socially conscious investors but also create a loyal customer base that shares their values.Investors increasingly recognize that ethical considerations can enhance portfolio performance while aligning with their values, ultimately leading to a more sustainable future.
The Future of Investment Management in a Changing Economy
The landscape of investment management is constantly evolving, driven by a multitude of economic trends and global events. As we look ahead, it is essential to understand how these factors are shaping the future of investment strategies and opportunities. The dynamics of globalization, technological advancements, and shifting consumer behaviors are creating new avenues for investors while also presenting challenges that require adaptability and foresight.Economic trends such as inflation, interest rate fluctuations, and geopolitical tensions have profound implications for investment management.
For instance, rising interest rates often lead to increased borrowing costs, which can dampen corporate profits and investment returns. Conversely, periods of low interest rates can spur economic activity and encourage higher valuations in equity markets. Additionally, global events such as pandemics or political unrest can disrupt supply chains and impact market stability, influencing investor sentiment and asset allocation decisions.
Understanding these interconnected factors is critical for investment managers aiming to optimize returns in a volatile environment.
Emerging Markets and Sectors for Investment Opportunities
Identifying sectors and markets that are poised for growth is paramount in the current economic climate. Emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Africa, present attractive opportunities for investors seeking diversification and growth potential. These regions often boast younger, rapidly expanding populations and increasing consumer spending, which can drive demand for goods and services. The technology sector, especially in areas such as fintech and renewable energy, is also gaining traction as countries pivot towards sustainable practices and digital transformation.Investors should consider the following emerging trends that highlight new opportunities in investment management:
| Trend | Description | Impact on Investment Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Green Investment | Focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria. | Increased demand for sustainable assets. |
| Digital Assets | Growth of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. | Emerging asset classes for diversification. |
| Healthcare Innovation | Advancements in biotechnologies and telehealth services. | Transforming traditional health investments. |
| Remote Work Solutions | Increased demand for technology enabling remote work. | Investment in software and communication platforms. |
| Supply Chain Resilience | Investment in technologies that enhance supply chain efficiency. | Focus on logistics and manufacturing sectors. |
Investors must remain vigilant and adaptive to capitalize on these emerging trends. By staying informed about global developments and shifts in consumer behaviors, investment managers can harness new growth opportunities while navigating the complexities of a changing economy.
“Investment management will thrive on innovation and adaptability in the face of global challenges.”
The Education and Skills Required for a Career in Investment Management
A successful career in investment management is built on a solid foundation of education and a suite of essential skills. As the financial landscape evolves, the need for professionals who can navigate complex investment vehicles and market dynamics becomes critical. This sector not only demands technical proficiency but also a keen understanding of market behaviors and client needs.Investment management professionals typically hold at least a bachelor’s degree in finance, economics, business administration, or a related field.
Many firms prefer candidates with advanced degrees, such as an MBA, which provides deeper insights into financial analysis and investment strategies. Nevertheless, practicality and experience in the field can outweigh formal educational credentials.
Essential Skills for Investment Management
To thrive in investment management, professionals need to cultivate several key skills that align with industry demands. These skills help in making informed decisions, managing risks, and building client relationships.
- Analytical Skills: The ability to analyze financial data and market trends is fundamental. Investment managers must assess various investment opportunities to determine their potential risks and returns.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is essential for conveying complex financial concepts to clients. Investment managers must articulate strategies clearly and persuasively.
- Attention to Detail: Precision is crucial in financial analysis, where minor errors can lead to significant repercussions.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The capacity to develop strategic solutions in response to evolving market conditions is invaluable.
- Technical Proficiency: Familiarity with financial modeling software and analytical tools enhances efficiency and accuracy.
Investment management is a dynamic field, necessitating continuous learning and professional development. Staying updated with market trends, economic shifts, and regulatory changes is vital. Participation in industry workshops, conferences, and seminars can significantly boost knowledge and networking opportunities.Aspiring investment managers can pursue several relevant certifications that enhance credibility and expertise, including:
- Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA): Highly regarded globally, this certification emphasizes investment analysis and portfolio management.
- Financial Risk Manager (FRM): Focuses on risk management in finance, equipping professionals with the tools necessary to manage potential market risks.
- Certified Financial Planner (CFP): Ideal for those looking to specialize in client-based financial planning and wealth management.
- Chartered Alternative Investment Analyst (CAIA): Designed for professionals who specialize in alternative investments, such as hedge funds and private equity.
By pursuing the right educational paths and certifications, individuals can effectively position themselves for success in the competitive field of investment management.
The Impact of Regulatory Frameworks on Investment Management Strategies
The investment management landscape is heavily influenced by regulatory frameworks that govern how investment firms operate. These regulations are designed to protect investors, maintain fair and efficient markets, and promote transparency within the financial system. Understanding the intricacies of these regulatory requirements is essential for investment managers, as they shape strategies, dictate compliance procedures, and influence overall market behavior.Regulations have a profound impact on investment management practices, often dictating the types of products offered, the manner in which assets are managed, and the reporting standards that must be adhered to.
One of the most significant regulations in recent years has been the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, enacted in response to the 2008 financial crisis. This legislation aimed to reduce risks in the financial system and improve transparency, which has led to a re-evaluation of risk management practices among investment managers. Compliance with such regulations necessitates adjustments in trading strategies, risk assessment methodologies, and operational processes, emphasizing the importance of regulatory awareness in investment decision-making.
Key Regulations Shaping Investment Management
Several pivotal regulations have shaped the investment management landscape significantly. These include:
- Investment Advisers Act of 1940: This act requires investment advisers to register with the SEC and adhere to fiduciary standards, mandating that they act in the best interest of their clients. This regulation has led to heightened accountability and transparency requirements for investment managers.
- MiFID II (Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II): Implemented in the EU, MiFID II enhances transparency in financial markets and impacts how investment firms operate, particularly regarding the handling of client information and the execution of trades. Compliance with MiFID II requires firms to adopt new trading practices and reporting standards.
- Basel III: This framework focuses on improving banking regulations worldwide, particularly concerning capital requirements and risk management practices. Though primarily aimed at banks, its implications extend to investment management as it influences funding availability and risk assessment strategies.
- ERISA (Employee Retirement Income Security Act): ERISA governs employee benefit plans and imposes fiduciary responsibilities on plan managers. This regulation has led to a focus on long-term investment strategies and transparency in fee structures.
Compliance with these regulations can lead to significant shifts in investment strategies. For instance, under the Investment Advisers Act, firms are required to conduct thorough due diligence before making investment recommendations. This means that an investment manager may need to forgo potentially lucrative opportunities if they do not align with a fiduciary duty to prioritize client interests.
“Compliance isn’t just about adhering to regulations; it’s about aligning business practices with ethical standards and client expectations.”
Additionally, regulations often necessitate the implementation of robust compliance frameworks, which can divert resources from investment decision-making to regulatory adherence. For example, the reporting requirements of MiFID II may compel firms to invest in technology to ensure accurate trade reporting, potentially limiting their ability to invest in alternative strategies or innovative financial products. As investment managers navigate the complexities of regulatory frameworks, the influence of these rules on their decision-making processes is undeniable, affecting everything from product offerings to risk management approaches.
Staying compliant not only fosters trust with clients but is also integral to sustainable investment management practices in today’s regulated environment.
Concluding Remarks
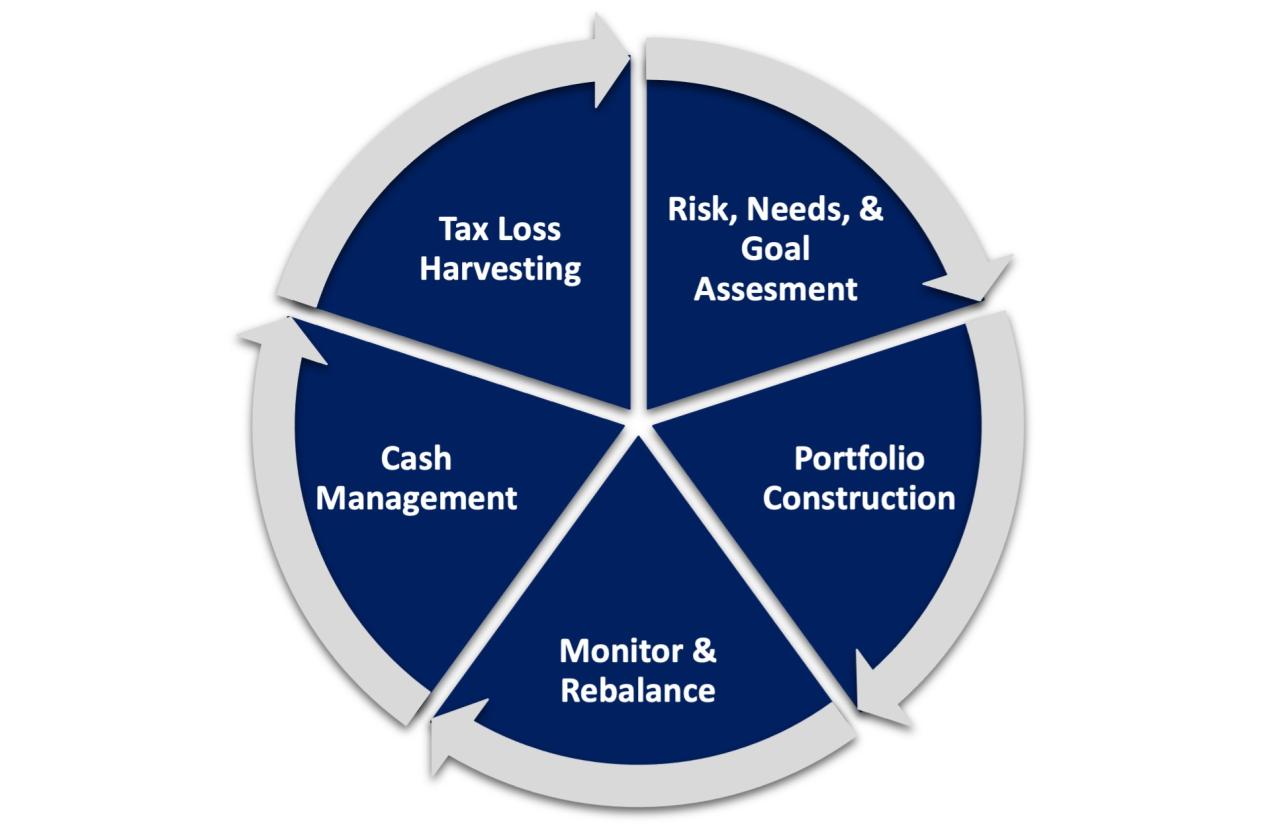
In conclusion, mastering the concepts of investment management equips individuals with the knowledge to make informed financial decisions. As we reflect on the various approaches, technological advancements, and ethical considerations, it’s clear that investment management is not just a profession but a vital component of personal finance. By adopting a proactive stance in their investment journeys, individuals can unlock new opportunities and secure their financial futures.
FAQ Corner
What is investment management?
Investment management involves the professional management of various securities and assets to meet specified investment goals for clients.
Why is diversification important in investment management?
Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across various assets, thus minimizing the impact of any one asset’s poor performance on the overall portfolio.
What are robo-advisors?
Robo-advisors are automated platforms that provide financial planning services with minimal human intervention, typically using algorithms to manage investment portfolios.
How often should I review my investment portfolio?
It’s generally advisable to review your investment portfolio at least annually, though significant life changes or market events may warrant more frequent evaluations.
What qualifications do I need for a career in investment management?
A degree in finance, economics, or a related field is typically required, along with certifications such as CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) for advanced career opportunities.